TRISS
What is the effect of lower Hemoglobin threshold for transfusion in patients with septic shock?
Study design

Population
- 998 patients (467 female, 531 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients in the ICU (ICU) who had septic shock and a Hgb concentration < 9 g/dL
- Key exclusion criteria: declined transfusion, previous adverse reaction to transfusion, received blood transfusion in ICU, ACS, life-threatening bleeding, and acute burn injury
Interventions
- N=502 restrictive blood transfusion therapy (1 unit of leukoreduced red cells when Hgb level < 7 g/dL)
- N=496 liberal blood transfusion therapy (1 unit of leukoreduced red cells when Hgb level < 9/dL)
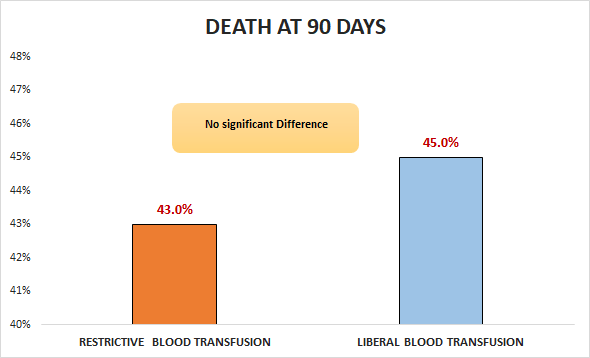
Primary outcome
Secondary outcomes
- No significant difference in use of life support at day 28
(16.1% vs. 19.9%; RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.54 to 1.09) - No significant difference in ischemic events in the ICU
(7.2% vs. 8%; RR 0.9, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.39)
Safety outcomes
No significant differences in severe adverse reaction (0% vs. 0.2%, p=1.00).
Conclusion
In patients in the ICU (ICU) who had septic shock and a Hgb concentration ≤ 9 g/dL, restrictive blood transfusion therapy was not superior to liberal blood transfusion therapy with respect to death at 90 days.
