Renal Arterial Resistive Index (RI)
The renal arterial resistive index (RI) is a sonographic measurement of intrarenal artery resistance, calculated as:
(Peak Systolic Velocity) - (End-Diastolic Velocity) / (Peak Systolic Velocity)
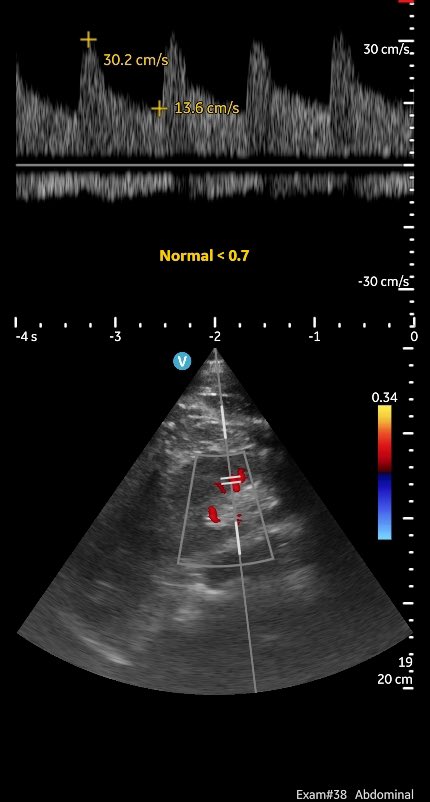
The normal RI range is 0.50-0.70. Elevated RI values are associated with poorer prognosis in various renal disorders and renal transplant outcomes.
Technique
RI is measured using spectral Doppler at either:
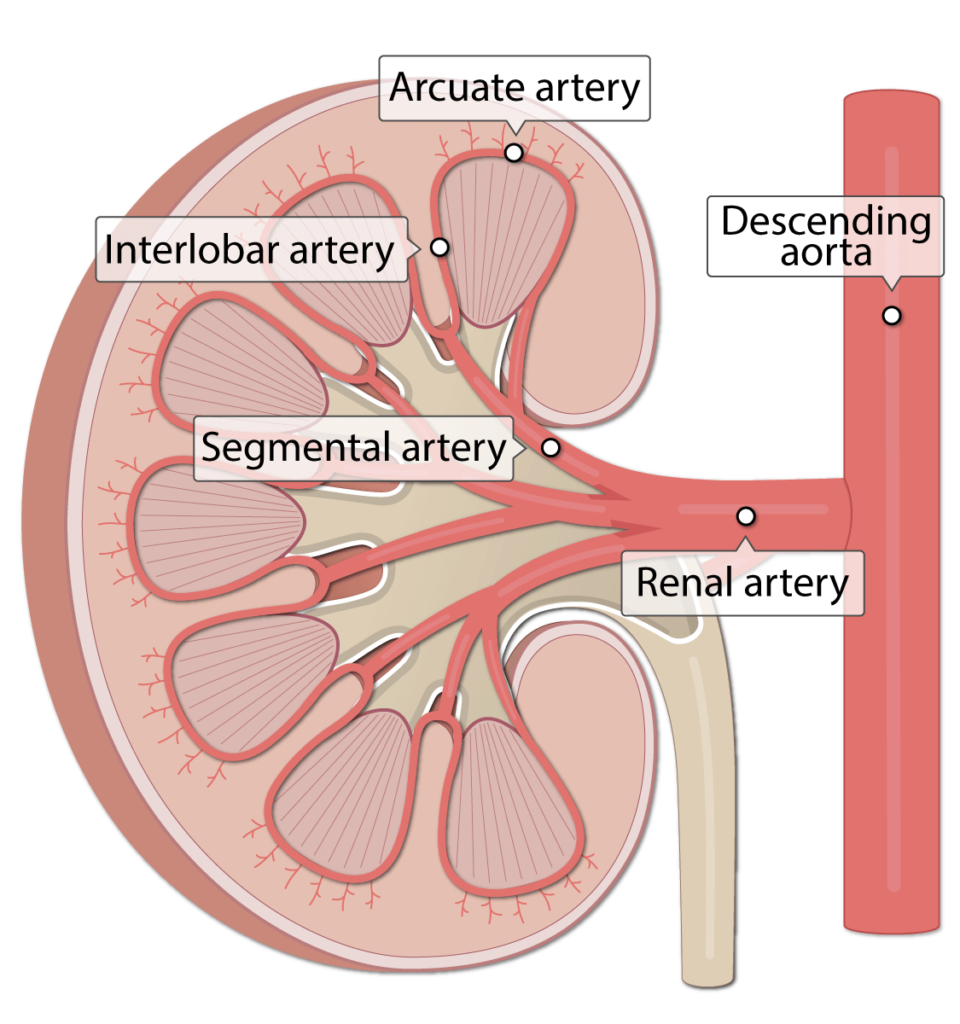
- Arcuate arteries (at the corticomedullary junction)
- Interlobar arteries (adjacent to medullary pyramids)
Significance
RI primarily reflects central hemodynamic factors (e.g., cardiac or aortic characteristics) rather than intrinsic renal properties. It indicates vascular compliance and pulsatility, often considered an “impedance index.”
High resistive indices (>0.8):
- In native kidneys: Associated with renal dysfunction and increased cardiovascular risk.
- In renal transplants: Linked to higher risk of graft loss and mortality.
Clinical Implications
Elevated RI Causes
- Medical renal disease
- Ureteric obstruction
- Extreme hypotension
- Young children
- Perinephric fluid collection
- Abdominal compartment syndrome
- Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
- Acute or chronic transplant rejection
- Renal vein thrombosis
- Drug toxicity
- Ureteric obstruction
- Perinephric fluid collection
Decreased RI Causes
- Renal artery stenosis
