PLATO
What is the effect of ticagrelor in patients with ACS?
Study design
Population
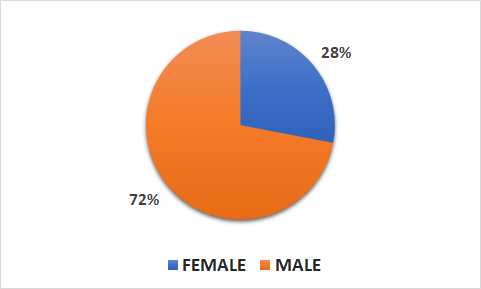
- 18624 patients
- Inclusion criteria: patients admitted to the hospital with an ACS, with or without ST-segment elevation
- Key exclusion criteria: any contraindication against the use of clopidogrel, fibrinolytic therapy within 24 hours before randomization, need for oral anticoagulation therapy, increased risk of bradycardia, and concomitant therapy with a strong cytochrome P-450 3A inhibitor or inducer
Interventions
- N=9333 ticagrelor (180 mg loading dose, 90 mg BID thereafter)
- N=9291 clopidogrel (300-600 mg loading dose, 75 mg daily thereafter)
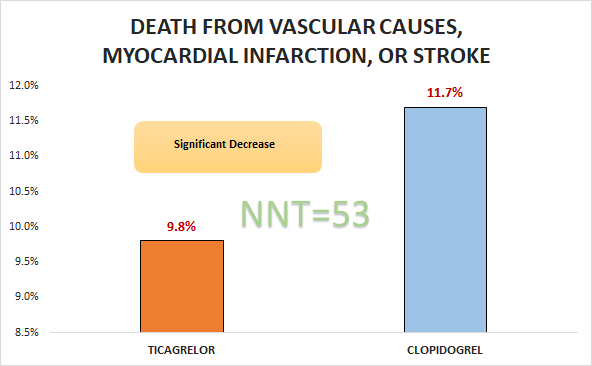
Primary outcome
Safety outcomes
- No significant differences in rates of major bleeding (11.6% vs. 11.2%, p=0.43).
- Significant differences in rates of major bleeding not related to CABG (4.5% vs. 3.8%, p = 0.03).
Conclusion
In patients admitted to the hospital with an ACS, with or without ST-segment elevation, ticagrelor was superior to clopidogrel with respect to death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
