CRISTAL
What is the effect of fluid resuscitation with colloids on mortality in critically ill patients presenting with hypovolemic shock?
Study design

Population
- 2857 patients (1075 female, 1782 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients admitted to the ICU with hypovolemic shock
- Key exclusion criteria: receipt of fluid therapy in the ICU, anesthesia-related hypotension, advanced chronic liver disease, chronic F, acute anaphylactic reaction, inherited coagulation disorders, pregnancy, dehydrated, or brain death or organ donor
Interventions
- N=1414 fluid resuscitation with colloids (gelatins, dextrans, hydroxyethyl starches, or 4% or 20% of albumin)
- N=1443 fluid resuscitation with crystalloids (isotonic or hypertonic saline or Ringer lactate solution)
Primary outcome
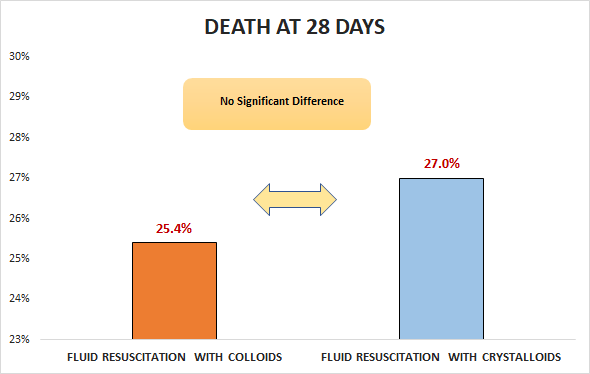
No significant difference in death at 28 days (25.4% vs. 27%; RR 0.96, 96% Cl 0.88 to 1.04)
Secondary outcomes
- Significant decrease in death at 90 days (30.7% VS. 34.2%; RR 0.92, 95% Cl 0.86 to 0.99)
- No significant difference in RRT (11% vs. 12.5%; RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.83 to 1.03)
Conclusion
In patients admitted to the ICU (ICU) with hypovolemic shock, fluid resuscitation with colloids were not superior to fluid resuscitation with crystalloids with respect to death at 28 days.
