CRANBERRIES FOR UTI
Effectiveness of cranberry products in preventing UTIs in susceptible populations
Study design
Systematic review and meta-analysis
Population
- Number of patients studied: 8,857
- Inclusion criteria: Susceptible populations including women with recurrent UTIs, children, elderly, pregnant women, and adults with bladder dysfunction
- Exclusion criteria: Studies not involving cranberry products for UTI prevention, non-randomized controlled trials, and quasi-RCTs
Interventions
- Experimental group: Cranberry products
- Control group: Placebo, no specific treatment, or other interventions (antibiotics, probiotics)
Primary outcome
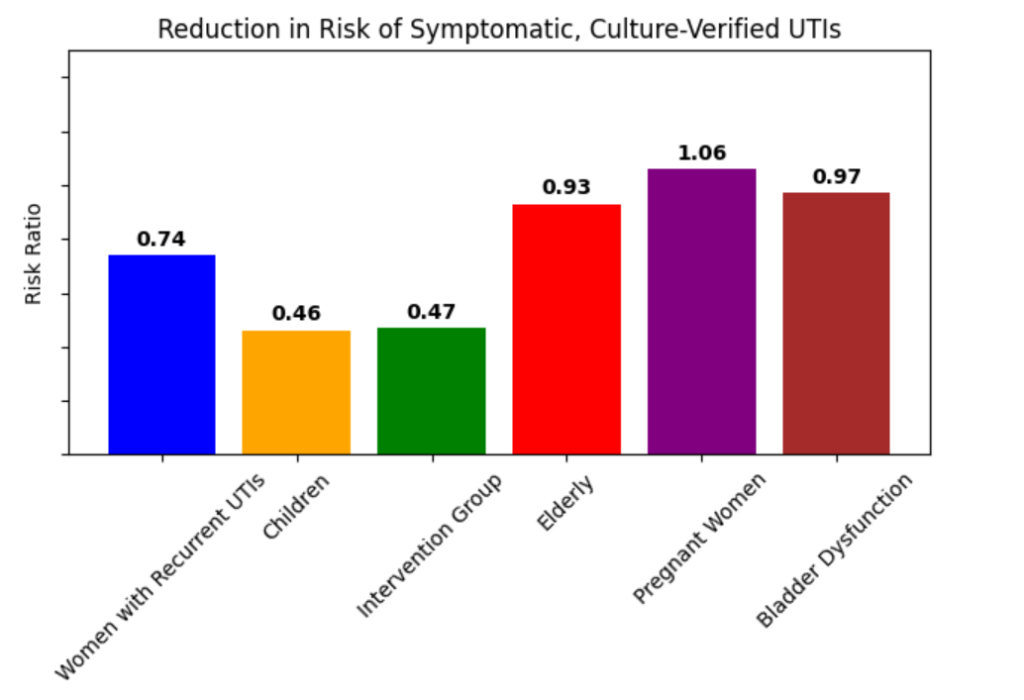
Significant difference? Yes, for women with recurrent UTIs, children, and people susceptible to UTIs following interventions. No significant difference for elderly, pregnant women, or adults with bladder dysfunction.
Secondary outcomes
Comparison of cranberry products to antibiotics, probiotics, different cranberry product forms (tablets, liquid), and different doses of PACs
Safety outcomes or Adverse Events
Gastrointestinal side effects: No significant difference between cranberry products and placebo or no specific treatment
Conclusion
Cranberry products reduce the risk of symptomatic, culture-verified UTIs in women with recurrent UTIs, children, and people susceptible to UTIs following interventions. No significant benefit for elderly, pregnant women, or adults with bladder dysfunction.
Study source: Jepson, R. G., Williams, G., & Craig, J. C. (2023). Cranberry products for the prevention of urinary tract infections. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 4, CD001321.
