Examining Inequity
“Not Otherwise Specified” host Lisa Rosenbaum talks with Marcella Alsan about her winding career path and her studies on medical mistrust, racial concordance between physicians and patients, and their effects on deeply entrenched health inequities
Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment and Medical Mistrust
- Reduction in healthcare demand and increased medical mistrust among older Black men
- Life expectancy at age 45 for Black men fell by up to 1.5 years
- 35% of life expectancy gap between Black and White older men in 1980
Research Study
- Conducted to understand the impact of race concordance between physicians and patients on uptake of preventative care services among Black men
- Two-stage design to disentangle the effects of trust and communication
- Pop-up clinic created and barbershops used for recruitment
Results
- Race concordance increased the uptake of preventative health services among Black men
- Trust and effective communication are important factors in healthcare
- Study ruled out discrimination, physician quality differences, and physician effort as explanations for observed differences
- More effective communication and rapport between race-concordant doctors and patients led to higher uptake of preventative care
- Importance of diversity and representation in healthcare to improve patient outcomes
Periorbital edema in dermatomyositis
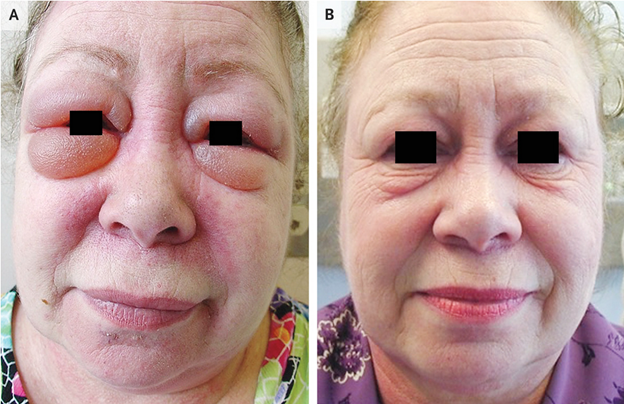
Presenting Symptoms
- 61 yo woman with a 6-month history of periorbital swelling
- Shoulder weakness
- No dyspnea, cough, or joint pain
Physical Examination Findings
- Erythema of upper and lower eyelids
- Substantial periorbital edema (Panel A)
- Midfacial erythema involving nasolabial folds
- Poikiloderma of the upper back
- 4/5 strength of shoulder abductors bilaterally
Laboratory and Imaging Results
- Creatine kinase: 6300 U/L (reference range, 24-170)
- Antinuclear antibody titer: 1:320
- Positive for anti-p155/140 myositis autoantibody
- MRI of right deltoid muscle: muscle edema
- Skin biopsy: interface dermatitis
Diagnosis
- Dermatomyositis
Characteristic Features
- Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy
- Immune-mediated muscle and skin injury
- Periorbital heliotrope rash with eyelid edema
- Shawl sign and malar rash not sparing nasolabial folds
Treatment
- Oral glucocorticoids
- Methotrexate
- Intravenous immune globulin
Cancer Screening
- Negative
Follow-up (2 months)
- Improvement in weakness, rashes, and periorbital edema (Panel B)
When to Get a Second Covid-19 Booster Shot
Challenges in Setting Vaccine Policy
- Changing pandemic landscape
- Pre-existing immunity from previous infections
- Variety of vaccines and schedules
- Reliance on observational data instead of trial data
- Changing prevalent variants
Vaccine Studies and Schedules
- Studies began 2.5 years ago
- Pfizer and Moderna studies concluded
- Difficulty interpreting data due to changing landscape
- Adaptation of vaccination policies
Immune Response and Variants
- Immunosuppressed patients may require more vaccinations
- Waning immunity and emergence of new variants (e.g., Omicron)
- Challenges understanding immune responses to different vaccines and variants
Vaccine Effectiveness and Boosters
- Vaccines effective in preventing hospitalization and death but protection wanes over time
- Boosting helps, but benefits decrease over time
- Focus on severe illness as the endpoint of interest
- Hybrid immunity benefits from prior vaccination and infection
RSV Vaccine
- Promising results for protecting older adults and infants
- Encouraging efficacy, further safety exploration needed
- RSV vaccine development shares similarities and differences with COVID vaccine development
- Vaccinating pregnant women can protect infants through passive antibody transfer
- Larger studies needed to assess safety and effectiveness in broader populations
Courts’ Disregard for Women’s Health and Safety — Intimate Partner Violence, Firearms, and “History and Tradition”
- Supreme Court decision in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association v. Bruen
- Struck down New York's restrictions on who may carry a firearm in public.
- Established a new approach for analyzing Second Amendment cases, focusing on "history and tradition."
- Impact on Violence Against Women Act (VAWA)
- U.S. District Court for the Western District of Texas and the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals struck down key VAWA protection.
- Held that VAWA's restriction on firearm possession by people subject to restraining orders is unconstitutional.
- Bruen's "history and tradition" analysis ignores the experiences of victims and survivors of intimate partner violence (IPV).
- Women's health and safety
- Legal protection for women's health and safety is relatively new.
- Restricting firearm access for domestic abusers has been shown to reduce IPV-related gun deaths.
- Recent court decisions have ignored evidence regarding the role of firearms in IPV-related injury and death.
- Expansion of VAWA
- Congress extended protections in VAWA for people experiencing IPV in 2022.
- Closed the "boyfriend loophole" by applying gun possession prohibition to all dating partners perpetrating IPV.
- Progress may be undermined by courts' regressive approach to women's health, safety, and equality.
- Role of medical and public health communities
- Crucial in calling out and countering the Court's erasure of facts and consequences of its decisions for victims of IPV.
Improving Care Integration for Dually Eligible Beneficiaries
Dual Eligibles
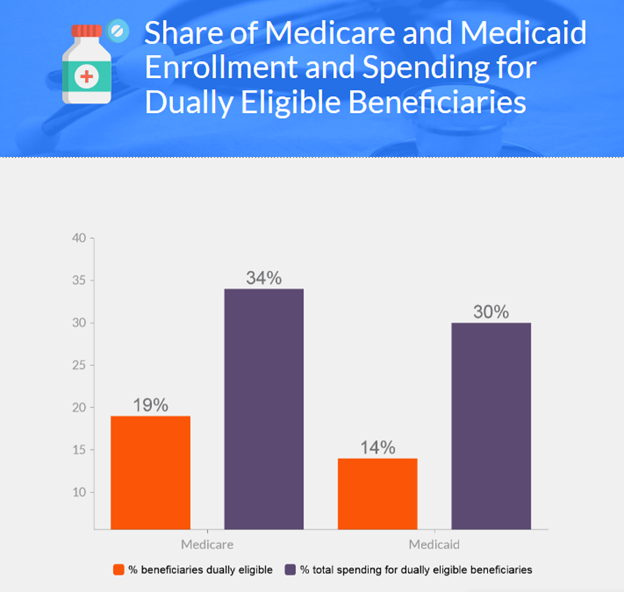
- 12.2 million people dually enrolled in Medicare and Medicaid
- Make up 19% of Medicare and 14% of Medicaid beneficiaries
- Account for approximately one third of spending in each program
Challenges
- Fragmented care and poor health outcomes due to inadequate coordination of benefits and services
Current Approaches for Care Integration
- State Medicare-Medicaid plans (MMPs)
- Federal Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE)
- Federal dual-eligible special-needs plans (D-SNPs)
Enrollment
- MMPs and PACE have strong care integration but low enrollment
- Over 4 million dual eligibles are enrolled in D-SNPs, with more than half in standard D-SNPs, which often have limited integration
- Only 10% of dually eligible beneficiaries are enrolled in strongly integrated care models
Possible Solutions
- Increase use of passive enrollment
- Improve program alignment
- Convert standard D-SNPs to FIDE-SNPs
- Improve data and measures used to evaluate care of dual eligibles
- Move toward a unified approach to integrated care
Treating Chronic Pain in Sickle Cell Disease — The Need for a Biopsychosocial Model
Chronic Pain in SCD
- Chronic pain is a common complication in adults with sickle cell disease (SCD) and affects their quality of life, functional ability, and healthcare utilization.
- The current approach to managing sickle cell pain is based mainly on a hematologic model, which is inadequate to address the complex nature of the disease.
- The biopsychosocial model of pain management helps to understand the role of biological, neuropsychological, and socioenvironmental elements in pain-related processes.
- Chronic pain in SCD is often affected by neuropsychological factors and requires a broader understanding of the experience of pain.
- The current healthcare system often dismisses the pain of adults with SCD, leading to a lack of pain relief, uncertainty about access to treatment, and a traumatic experience for patients.
- The medical community needs to recognize the impact of patients' interactions with the healthcare system on their pain and invest in a biopsychosocial approach to pain management.
- A biopsychosocial approach to pain management in SCD includes mindfulness-based pain management, educational strategies, psychological services, prompt access to acute pain management, respectful and compassionate treatment, and more.
Components of a Biopsychosocial Approach to Pain Management in SCD
- Mindfulness-based pain management training
- Educational strategies to empower patients
- Psychological services based on patient need
- Clinical pain management approach based on validation of the patient's experience
- Prompt and unimpeded access to acute pain management
- Respectful and compassionate treatment throughout the healthcare system.
Bempedoic Acid and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Statin-Intolerant Patients
Background
- Bempedoic acid is an ATP citrate lyase inhibitor that reduces LDL cholesterol levels
- Associated with a low incidence of muscle-related adverse events
- Statins are the cornerstone of contemporary therapy to lower LDL cholesterol
- 7-29% of patients report adverse musculoskeletal effects from statins, leading to withdrawal
- Bempedoic acid targets cholesterol synthesis upstream of the enzyme inhibited by statins
- Similar to statins, it reduces hepatic cholesterol synthesis and raises LDL receptor expression
- Prodrug activated in the liver, not in most peripheral tissues, potentially reducing muscle side effects
- Approved by FDA and European Medicines Agency after LDL cholesterol reduction in studies
- No randomized, controlled trials on bempedoic acid's effects on cardiovascular events
- CLEAR Outcomes trial conducted to determine bempedoic acid's effects on adverse cardiovascular events in statin-intolerant patients
Methods
- Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
- Conducted at 1250 sites in 32 countries
- Sponsored by Esperion Therapeutics, in collaboration with Cleveland Clinic Coordinating Center for Clinical Research (C5Research) and an academic executive committee
- Patients aged 18-85 years with increased cardiovascular risk, "statin-intolerant"
- 4-week run-in period with single-blind placebo
- Randomized 1:1 to receive bempedoic acid (180 mg daily) or placebo
- Primary endpoint: composite of major adverse cardiovascular events (time-to-first-event analysis)
- Key secondary endpoints: various cardiovascular events and death from any cause
- At least 90% power to detect a 15% reduction in relative risk of primary endpoint event
- Required minimum of 1620 primary endpoint events and 810 key secondary endpoint events
- Cox proportional-hazards model for efficacy analysis, using intention-to-treat principle
Results
- 13,970 patients randomized; 6992 in bempedoic acid group and 6978 in placebo group
- Median follow-up of 40.6 months
- Bempedoic acid led to greater reduction in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity CRP levels
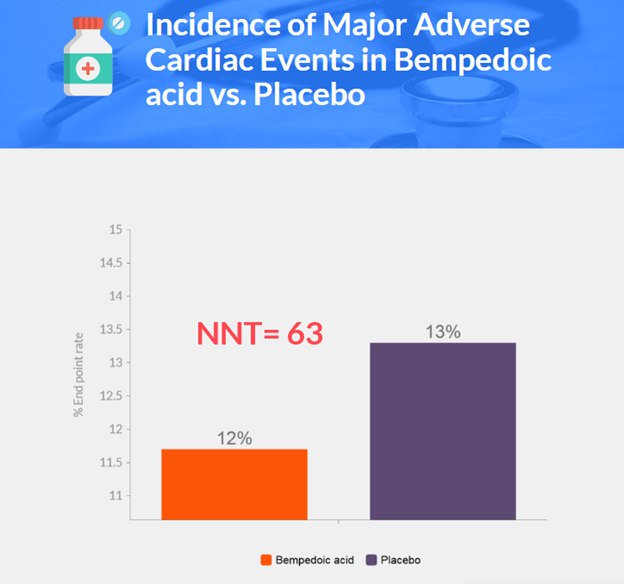
- Primary endpoint: 11.7% in bempedoic acid group vs. 13.3% in placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.87; p=0.004)
- First three key secondary endpoints significantly lower in bempedoic acid group
- No significant difference in other key secondary endpoints
- Adverse events similar in both groups, except for elevations in hepatic-enzyme levels and renal events
- Bempedoic acid group: higher incidence of hyperuricemia, gout, and cholelithiasis
Discussion
- Bempedoic acid lowered the risk of primary end-point events by 13% compared to placebo after 40.6 months of follow-up.
- First three key secondary end points showed significant benefits with bempedoic acid over placebo.
- Bempedoic acid led to few adverse events, and discontinuation rates were similar to placebo.
- Bempedoic acid may be an alternative LDL cholesterol-lowering therapy for patients unable or unwilling to take statins.
- Effects of bempedoic acid on cardiovascular outcomes were similar to other nonstatin therapies.
- Bempedoic acid did not increase glycated hemoglobin levels or incidence of new-onset diabetes.
- Bempedoic acid showed a 21.6% reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels relative to placebo.
- The trial included patients for primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease who were unable or unwilling to take statins.
- Limitations: the study only included patients unwilling or unable to take statins and did not examine effects in populations with lower LDL cholesterol levels or those taking conventional statin doses.
Tranexamic Acid to Prevent Obstetrical Hemorrhage after Cesarean Delivery
Background
- Postpartum hemorrhage accounts for 27.1% of maternal deaths globally and is the second most common cause of pregnancy-related death in the US.
- Tranexamic acid, a fibrinolysis inhibitor, has been shown to reduce mortality in bleeding trauma and obstetrical hemorrhage patients.
- Increased fibrinolytic activity observed post-delivery; tranexamic acid could potentially improve hemostasis by preventing clot breakdown.
- Previous studies on tranexamic acid for preventing obstetrical hemorrhage are limited by small sample sizes and single-center designs.
- Two large, multicenter trials did not show significant reduction in postpartum hemorrhage incidence or major clinical outcomes with tranexamic acid use.
- Neither of the two previous trials were powered to detect differences in blood product transfusion incidence.
- New randomized trial aims to assess tranexamic acid's effect on maternal death or blood transfusion risk in cesarean deliveries.
Methods
- Multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial conducted at 31 hospitals.
- Trial approved by institutional review boards, with informed consent obtained from participants.
- Inclusion criteria: scheduled or unscheduled cesarean delivery of singleton or twin gestation.
- Key exclusion criteria: maternal age <18, certain medical conditions, contraindications to tranexamic acid, or planned transfusion/antifibrinolytic agents.
- Participants randomized 1:1 to receive 1g tranexamic acid or placebo after umbilical-cord clamping.
- Primary outcome: composite of maternal death or blood transfusion before discharge or 7 days postpartum.
- Major secondary outcome: estimated intraoperative blood loss >1 liter.
- Other secondary outcomes: treatments/interventions for bleeding complications, infectious complications, change in preoperative-to-postoperative hemoglobin levels, and maternal thromboembolic events.
- Statistical analysis conducted with the intention-to-treat principle.
- Sample size: 11,000 participants (5,500 per group) for 85% power to detect a 33% lower risk of primary outcome in tranexamic acid group at a two-sided type I error of 5%.
Results
- 84,062 patients screened for randomization; 11,000 patients randomized (5529 tranexamic acid group, 5471 placebo group).
- Baseline characteristics similar between groups, except preoperative hemoglobin level below 8 g/dL more common in placebo group.
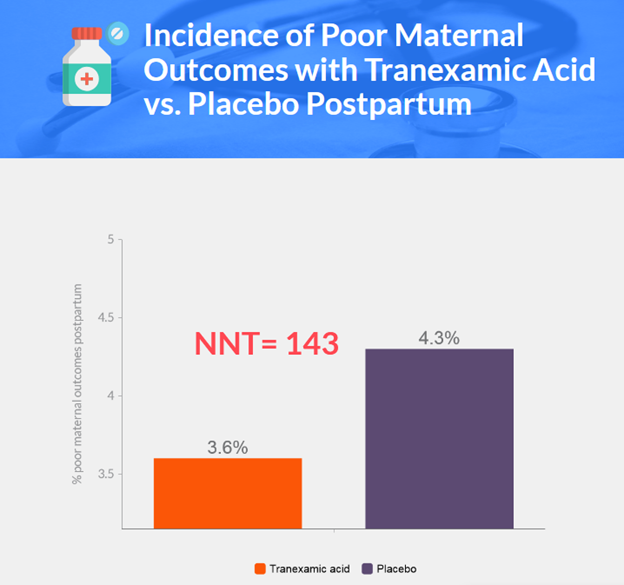
- Primary outcome: 3.6% in tranexamic acid group, 4.3% in placebo group (adjusted relative risk 0.89; 95.26% CI, 0.74-1.07; P=0.19).
- Estimated intraoperative blood loss >1 liter: 7.3% in tranexamic acid group, 8.0% in placebo group (relative risk 0.91; 95% CI, 0.79-1.05).
- Composite of treatments/interventions for bleeding complications: 16.1% in tranexamic acid group, 18.0% in placebo group (relative risk 0.90; 95% CI, 0.82-0.97).
- Mean preoperative-to-postoperative change in hemoglobin level: -1.8 g/dL in tranexamic acid group, -1.9 g/dL in placebo group (mean difference -0.1 g/dL; 95% CI, -0.2 to -0.1).
- Postpartum infectious complications: 3.2% in tranexamic acid group, 2.5% in placebo group (relative risk 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.61).
- No significant differences in major safety outcomes, including thromboembolic events or new-onset seizure activity.
Discussion
- Prophylactic use of tranexamic acid during cesarean delivery did not significantly lower the risk of maternal death or blood transfusion
- No significant difference was found in the incidence of estimated intraoperative blood loss of more than 1 liter
- Treatments and surgical interventions in response to bleeding and related complications occurred in a similar proportion of participants in both groups
- The risk of thromboembolic events was not higher in the tranexamic acid group than in the placebo group
- Previous observational studies and systematic reviews suggested a reduction in blood transfusion with prophylactic tranexamic acid, but this trial did not find a significant difference in the use of blood transfusion
- This trial was larger than previous trials and was adequately powered to evaluate the effect on the use of blood transfusion
- Limitations include unknown benefit of earlier administration, exclusion of high-risk patients, and unexpected higher incidence of postpartum infections with tranexamic acid.
Dersimelagon in Erythropoietic Protoporphyrias
Background
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria and X-linked protoporphyria are rare genetic photodermatoses
- Deficiency of ferrochelatase or increased activity of erythroid-specific δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase 2 results in overproduction of photoactive metal-free protoporphyrin
- Patients typically present in childhood with excruciating phototoxic attacks, primarily affecting the face and the dorsum of the hands
- These disorders are vastly underrecognized and often have a diagnostic delay of more than a decade
- Photoprotective clothing is beneficial, and sunlight avoidance becomes the primary mode of symptom prevention
- Afamelanotide is currently the only treatment approved to increase sunlight tolerance in adults with erythropoietic protoporphyria
- Dersimelagon is a new orally administered selective melanocortin 1 receptor agonist that activates eumelanin production for photoprotection and antioxidative effects
- A phase 1 study showed an acceptable safety profile for dersimelagon
- A randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial was conducted to investigate the efficacy and safety of dersimelagon in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria or X-linked protoporphyria
- The trial assessed the time to the first prodromal symptom during sunlight exposure and analyzed levels of melanin as a direct marker of the mechanism of action of dersimelagon
Methods
- The trial was conducted at nine sites in the United States, with a 2-week screening period, 16-week treatment period, and 6-week follow-up period
- Trial participants attended in-clinic visits at weeks 4, 8, 12, and 16, with in-clinic sunlight-exposure tests performed before randomization and at week 16
- Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to take placebo, 100 mg of dersimelagon, or 300 mg of dersimelagon orally once daily in the morning with food
- The primary efficacy end point was the change from baseline to week 16 in the time to the first prodromal symptom associated with sunlight exposure, with secondary end points including the number of sunlight-exposure episodes with prodromal symptoms and the number of phototoxic pain events during the 16-week treatment period
- Quality of life was assessed with the PROMIS-57 questionnaire and the PGI-C scale, with changes in melanin density and erythrocyte protoporphyrin levels also assessed
- Patients’ knowledge of their assigned treatment group was assessed at the end of the trial
- Safety data included adverse events recorded continuously and nevi evaluation at baseline, weeks 8 and 16, and at the end of the trial
- The primary end point was analyzed in the intention-to-treat population using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures, with safety analyzed in the safety population
Results
- 102 patients underwent randomization; 35 received placebo, 33 received 100mg dersimelagon, and 34 received 300mg dersimelagon.
- 90% of patients completed the treatment period; 10% discontinued early.
- Patient characteristics were well-balanced among treatment groups, except for a sex imbalance.
- Dersimelagon significantly increased the mean daily time to the first prodromal symptom associated with sunlight exposure compared to placebo.
- Patients receiving dersimelagon had lower incidence rates of sunlight-exposure episodes with prodromal symptoms and phototoxic pain events compared to those receiving placebo.
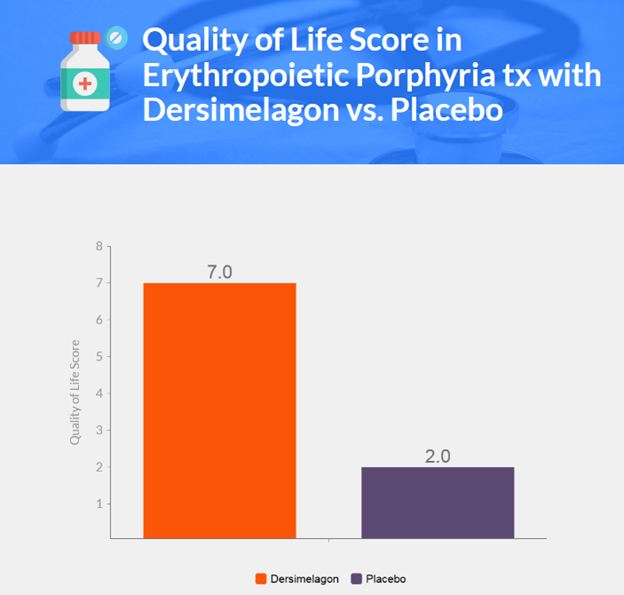
- Quality of life was better among patients receiving dersimelagon than those receiving placebo.
- Adverse events were mostly mild or moderate in severity and resolved within the trial period; the most frequent were nausea, freckles, headache, and skin hyperpigmentation.
- No clinically significant changes were noted in hematologic measures, biochemical measures, coagulation, or urinalysis test results in all groups.
Discussion
- Dersimelagon at 100 mg or 300 mg daily increased time to first prodromal symptom with sunlight exposure in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria or X-linked protoporphyria compared to placebo
- Sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of the parametric model with some missing data for the primary endpoint
- Improvements were seen in several secondary efficacy endpoints with dersimelagon treatment
- The use of a patient-reported primary endpoint is valuable for assessing the efficacy of treatment for erythropoietic protoporphyria or X-linked protoporphyria
- Both doses of dersimelagon were effective and had acceptable side-effect profiles, without hepatic toxic effects
- Dose-dependent increases in the frequency of treatment-related effects on the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and gastrointestinal tract suggest that a dose of less than 300 mg could be used in a subsequent phase 3 trial
- Limitations of the study include lack of formal statistical power analysis, small sample size, lack of long-term follow-up, and lack of patient racial and ethnic diversity
- Results support the effectiveness and safety of dersimelagon as a potential oral treatment option for increasing light tolerance in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria or X-linked protoporphyria.
Effect of Donor Sex on Recipient Mortality in Transfusion
Background
- Observational evidence suggests characteristics of blood donors affect transfusion recipient outcomes
- Donor sex may affect outcomes but biologic mechanisms are unclear
- Storage-associated hemolysis in stored red cells may be dependent on donor characteristics
- Sex-related differences in red-cell properties may contribute to recipient outcomes
- Observational evidence is conflicting on whether donor sex affects recipient outcomes
- Red-cell transfusion is a frequent medical treatment with over 100 million units obtained worldwide annually
- The iTADS trial investigates whether a transfusion strategy involving predominantly female donors would lead to different recipient outcomes as compared with a strategy involving predominantly male donors among all hospital patients receiving a transfusion
Methods
- Double-blind, pragmatic, randomized trial conducted at three academic sites in Canada
- Eligible patients randomly assigned in a 60:40 ratio (male donor group to female donor group) to receive red-cell transfusion from either a male donor or female donor
- All red-cell units assigned by the hospital blood banks and data collected from routinely collected clinical and administrative data
- Trial investigators, medical teams, blood-bank staff, and patients were unaware of the trial-group assignments
- Data collection and follow-up conducted by the Ottawa Hospital Data Warehouse infrastructure, Canadian Blood Services, and ICES
- Primary outcome was survival, and secondary outcomes included survival at various time intervals, duration of hospital stay, and occurrence of adverse events
- Intention-to-treat approach used for all analyses, and subgroup analyses conducted based on various factors
- Statistical analysis conducted using SAS and R software
Results
- 13,047 patients were randomized, 8719 patients (3529 in the female donor group and 5190 in the male donor group) were included in the analysis.
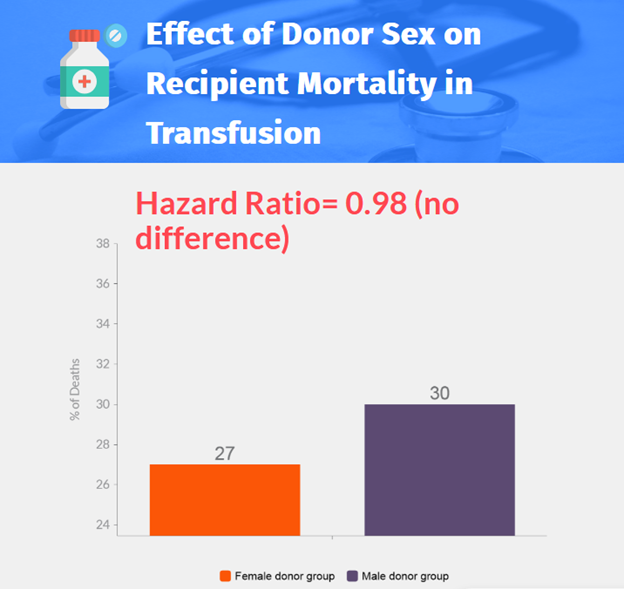
- No significant difference was found in survival between the female donor group and the male donor group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.91 to 1.06).
- There were no significant differences in secondary outcomes except for a higher incidence of MRSA infection in the female donor group.
- Subgroup analyses suggested a lower risk of death among male patients assigned to the female donor group and a higher risk of death among recipients of red-cell units from female donors aged 20 to 29.9 years.
- Post hoc analysis showed fewer deaths among recipients of transfusions of red cells from donors mismatched for sex.
Discussion
- No overall survival benefit was found in the trial for red-cell transfusion from a male donor compared with a female donor
- Subgroup effects observed were inconsistent and may have been due to chance
- Observational studies have shown conflicting associations between donor sex and transfusion outcomes
- Large, randomized trials are necessary to definitively answer questions about transfusion outcomes
- The trial had several strengths, including its size and representation of the population at risk
- Limitations of the trial included nonadherence and potential differences in blood-banking practices in other jurisdictions
- No significant difference in survival was found between the two transfusion strategies
Air Pollution and Mortality at the Intersection of Race and Social Class
Background
- Exposure to air pollution containing fine particulate matter (PM2.5) increases the risk of premature death.
- The EPA sets National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for PM2.5 to protect public health and requires states to ensure concentrations fall below prescribed levels.
- The current NAAQS for annual average PM2.5 levels is 12 μg per cubic meter.
- Studies have shown adverse health effects at levels below 12 μg per cubic meter, particularly among marginalized subpopulations such as low-income and Black Americans.
- Lowering the PM2.5 NAAQS would generate substantial benefits for the health of the nation, but currently available evidence is insufficient to estimate the health benefits effectively.
- Previous studies have not considered effects among subpopulations defined by both racial and ethnic identity and socioeconomic position, assumed a linear exposure-response curve, and not implemented causal inference methods to estimate exposure-response curves.
- The authors analyzed data from more than 73 million Medicare enrollees to estimate potentially nonlinear exposure-response curves for PM2.5 exposure and mortality for the full study population and for marginalized subpopulations.
- The authors hypothesized that exposure-response curves would differ between subpopulations and that exposure-response slopes would be steeper among more marginalized subpopulations.
Methods
- The study population included all Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 or older enrolled from 2000 through 2016.
- Data on age, sex, race or ethnic group, Medicaid eligibility, date of death, and residential ZIP Code were obtained from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
- Racial and ethnic identities were obtained from beneficiary-reported data using a single variable instrument with seven mutually exclusive categories.
- The study focused on Black and White beneficiaries due to substantial misclassification of other racial and ethnic identities in CMS data.
- Socioeconomic position was defined on the basis of income, with low-income persons defined as those eligible for any Medicaid benefits.
- PM2.5 exposure estimates were obtained using a well-validated exposure prediction model that provides estimated daily PM2.5 levels at a 1-km2 grid scale across the contiguous United States.
- Confounding variables, including sociodemographic, meteorologic, and health-behavior variables, were adjusted for in the statistical analysis.
- Stratum-specific mortality data was calculated, with strata defined jointly according to age, sex, race, Medicaid eligibility, and follow-up year.
- An established causal inference method was used to estimate exposure-response curves, hazard ratios, and 95% confidence intervals for the full Medicare population and for race-by-income subpopulations.
- Sensitivity analyses were conducted using other methods.
Results
- The study population included over 73 million Medicare beneficiaries enrolled from 2000 through 2016.
- The mean average annual PM2.5 exposure during the study period was 9.8 μg per cubic meter across the full population, with Black persons exposed to higher levels than White persons.
- Lowering PM2.5 exposure from 12 μg per cubic meter to 6 μg per cubic meter was associated with a decreased hazard ratio for death, with the exposure-response curve between 6 and 12 μg per cubic meter appearing approximately linear.
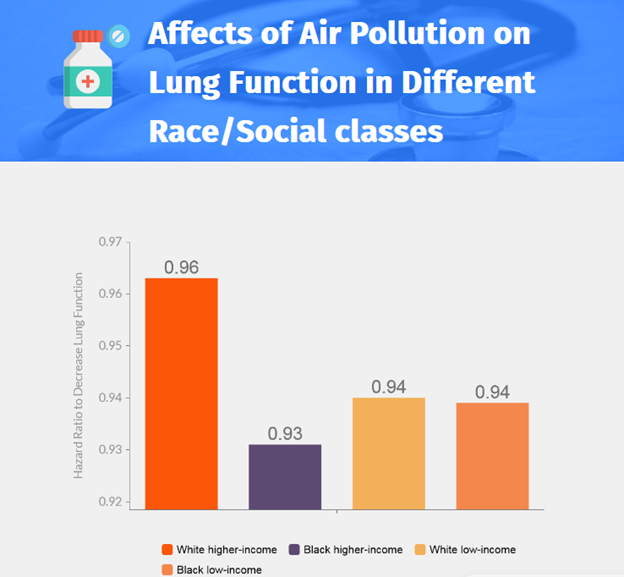
- Exposure-response curves differed between some subpopulations, with estimates of the hazard ratio for death dropping faster for Black persons than for White persons as the annual average PM2.5 exposure decreased.
- Among higher-income beneficiaries, the exposure-response slope was steeper for Black persons than for White persons, with the decrease in mortality associated with a decrease from 12 μg per cubic meter to 8 μg per cubic meter nearly double for Black persons as compared with White persons.
- In contrast, exposure-response curves for both Black and White low-income persons appeared mostly linear and nearly identical between 6 and 12 μg per cubic meter.
Discussion
- Lowering PM2.5 levels would benefit all aging Americans, regardless of racial identity or socioeconomic position
- Racial identity and socioeconomic position may combine to alter exposure–response curves for long-term PM2.5 exposure and mortality
- Black higher-income, Black low-income, and White low-income persons may benefit more from a lower PM2.5 NAAQS than White higher-income persons
- A lower PM2.5 NAAQS may reduce environmental inequities among a broad swath of Americans marginalized by structural racism and social exclusion and disproportionately affected by air pollution
- The study findings suggest that a comparatively lower annual PM2.5 NAAQS will lead to larger reductions in mortality among older Americans and produce greater health benefits among a wider array of disproportionately affected Americans than previously recognized
- The EPA public health and environmental justice–seeking mandates may require considerably stronger NAAQS for annual PM2.5 (e.g., ≤8 μg per cubic meter)
Screening for Prostate Cancer

Epidemiology
- Prostate cancer is the most diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death among U.S. men.
- The incidence and mortality rates are highest among older men, with the incidence greatest among men in their 70s and mortality highest among men in their 80s.
- Incidence and mortality are lower among Hispanic men and Asian men than among White men and non-Hispanic Black men.
- Non-Hispanic Black men have 1.7 times higher incidence and 2.1 times higher mortality rates compared to non-Hispanic White men.
Screening
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening should involve shared decision making with consideration of the risks and benefits of screening and patient preferences.
- Randomized trials support a modest reduction in prostate cancer mortality with PSA screening.
- Persons with elevated PSA levels on screening may choose to undergo further tests to inform the need for biopsy, multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to identify biopsy targets, or both.
- Persons with low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer may choose to undergo active surveillance (periodic PSA tests and biopsies) over immediate curative treatment (surgery or radiation therapy).
- Surgery and radiation therapy generally provide excellent outcomes in prostate cancer but may result in harms, including urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction with surgery, and bowel dysfunction and erectile dysfunction with radiation therapy.
PSA
- The onset of widespread PSA screening in the late 1980s is widely acknowledged to be the primary cause of the sharp increase in prostate cancer incidence that was observed in the next decade.
- Rates later fell, beginning in approximately 2009.
- The association between PSA screening and mortality is less clear than the association between screening and incidence.
- There is no PSA level below which prostate cancer can be definitively ruled out.
Randomized Controlled Trials
- The European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC) showed a reduction in prostate cancer mortality with PSA screening.
- The Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) trial and the U.K. Cluster Randomized Trial of PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer (CAP) trial showed no significant difference in prostate cancer mortality between the intervention and control groups.
- Systematic reviews of PSA screening trials have noted a high risk of bias in the PLCO trial owing to contamination of the control group and in the CAP trial owing to low adherence to screening.
Conservative Management or Curative Treatment
- The SPCG-4 and PIVOT trials showed a lower incidence of death from prostate cancer with surgery than with observation, with a higher risk at baseline among men in the SPCG-4 trial.
- The ProtecT trial showed no significant difference in prostate cancer mortality among the groups, but the rate of metastases was significantly higher with active monitoring.
Harms Associated with PSA Screening
- The cumulative percentage of false positive PSA results is estimated to be between 10% and 15% over several rounds of screening, with approximately a 5% risk of a false positive screen with a subsequent negative biopsy.
- Prostate biopsy is associated with complications such as infection, hematuria, rectal bleeding, urinary obstruction or retention, and transient erectile dysfunction.
- Screening results in substantial overdiagnosis, with an estimated 23 to 42% of prostate cancer cases detected by screening being overdiagnosed.
Management Strategies for Positive Screens
- Initial steps include a repeat of the screening test and assessment of the possibility of transient or treatable causes of PSA elevation.
Coffee Bean Sign in Cecal Volvulus
Patient information
- 87-year-old man with chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation
Chief complaint and physical examination
- Presented with constipation and lower abdominal pain
- Physical exam showed abdominal distention and tenderness in the right lower quadrant
Imaging findings
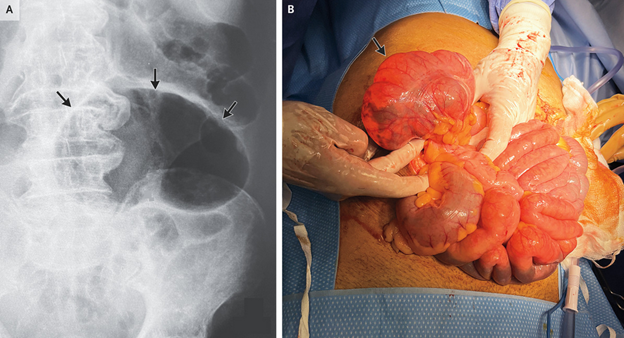
- Plain radiograph showed an air-filled loop of large bowel resembling a coffee bean, indicating cecal volvulus
Diagnosis and treatment
- Successful detorsion performed, but cecopexy and cecostomy were needed due to hemodynamic instability
Follow-up
- At 6-month follow-up, patient was doing well and declined ostomy reversal.
A 67-Year-Old Man with Mantle-Cell Lymphoma and Hypoxemia
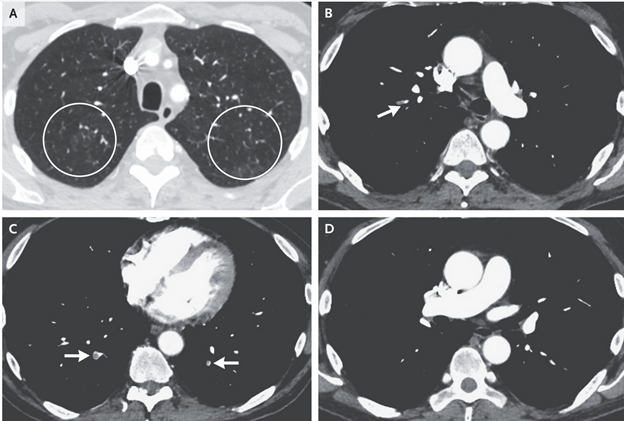
Case
- 67-year-old man with history of duodenal adenocarcinoma, pulmonary embolism, and mantle-cell lymphoma admitted for hypoxemia
- CT pulmonary angiography revealed pulmonary emboli and pulmonary nodules
- Complex medical history suggests numerous possible pulmonary diseases
Differential Diagnosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary infection (community-acquired or opportunistic)
- Chemotherapy-induced pneumonitis
- Lung involvement from malignancies (duodenal adenocarcinoma, mantle-cell lymphoma)
- Shunt
Evaluation
- Patient had hypoxemia that did not improve with supplemental oxygen, suggesting the presence of a physiological shunt
- Chest imaging did not show an apparent shunt, leading to a suspicion of methemoglobinemia
- Methemoglobinemia confirmed by measurement of blood methemoglobin level, likely caused by dapsone
Treatment
- Patient treated with intravenous methylene blue, leading to prompt resolution of hypoxemia
- Transthoracic echocardiogram showed only trace right-to-left shunting through patent foramen ovale, unlikely to fully explain hypoxemia
Final Diagnosis
- Dapsone-induced methemoglobinemia.
Benefits of Bempedoic Acid — Clearer Now
Vascular Atherosclerosis and Statins
- Vascular atherosclerosis begins in young adulthood and progresses over decades.
- Associated with morbidity and mortality from coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral vascular disease.
- Statins lower LDL cholesterol, slow atherosclerosis progression, and reduce morbidity and mortality associated with vascular events.
- High-intensity statin therapy recommended for patients with established atherosclerotic vascular disease and those at high risk.
Alternatives to Statins
- Approximately 10% of patients unable or unwilling to take statins, primarily due to muscle-related symptoms.
- Alternatives include ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors, and bempedoic acid.
- Ezetimibe has modest effect in lowering LDL cholesterol and risk of cardiovascular events.
- PCSK9 inhibitors are highly effective at lowering LDL cholesterol but require parenteral administration and are expensive.
Bempedoic Acid
- Inhibitor of ATP citrate lyase, works upstream of statins in the same mechanistic pathway.
- Reduces LDL cholesterol when used alone or in combination with ezetimibe or statins in statin-intolerant patients or those with familial hypercholesterolemia.
- Metabolized in the liver but not in peripheral tissues, resulting in few muscle-related side effects.
- Lacked high-quality evidence for reducing risk of clinical events until the CLEAR Outcomes trial.
CLEAR Outcomes Trial
- 13,970 patients with or at high risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease unable to take more than a very low dose of statin were randomly assigned to receive bempedoic acid (180 mg daily) or placebo.
- Bempedoic acid showed a greater reduction in LDL cholesterol by 21 percentage points and 13% lower risk of primary composite end point over a median of 3.4 years.
- Reduced risk of secondary end-point events, including death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
- Similar effects observed in patients using concomitant ezetimibe and very-low-dose statins.
- No significant difference in percentage of patients with myalgias; however, higher incidences of gout, cholelithiasis, and laboratory elevations in creatinine, uric acid, and hepatic enzyme levels.
Implications and Future Research
- Bempedoic acid now an evidence-based alternative to statins for primary and secondary prevention in high cardiovascular risk patients.
- Should not be considered an alternative to statins due to overwhelming evidence of vascular benefits of statins.
- Two observations warrant further exploration: greater effect in primary-prevention cohort and no observed effect on mortality.
- Clinicians should continue to prescribe statins at maximum tolerated doses and focus on better primary and secondary prevention for at-risk patients.
Bempedoic Acid and the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease- Science Behind Study
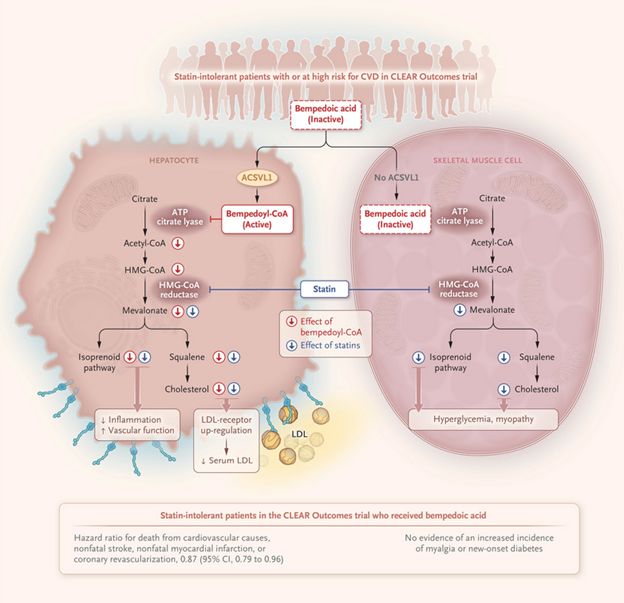
CLEAR Outcomes Trial
- Tested bempedoic acid in patients with or at increased risk for cardiovascular disease
- Targeted statin-intolerant patients
- Result: 21 percentage points greater reduction in LDL cholesterol levels with bempedoic acid compared to placebo
- Corresponded to a 13% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events
Statins Mechanism of Action
- Inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme of the mevalonate pathway responsible for cholesterol and isoprenoid synthesis
- Statins produce intracellular cholesterol depletion, up-regulating LDL receptors to internalize more cholesterol
- Can lower LDL cholesterol levels by 30 to 50%, but can have side effects like elevated blood sugar levels and myopathy
Bempedoic Acid Mechanism of Action
- Requires conversion by ASCVL1 into an active metabolite
- Inhibits the mevalonate pathway and up-regulates hepatic LDL receptors to lower circulating LDL cholesterol levels
- Theoretical advantages: only active in tissues that express ASCVL1, potentially avoiding myopathic symptoms or hyperglycemia
Comparing Bempedoic Acid and Statins
- Statins have proven track record in preventing cardiovascular disease
- Bempedoic acid monotherapy lowers LDL cholesterol levels up to 28%
- Choice between the two would likely arise in patients with statin-associated adverse effects
Side Effects and Drug Interactions
- Bempedoic acid may avoid peripheral side effects like diabetes and myopathy seen in statins
- However, combining bempedoic acid with a statin may enhance the occurrence of muscle symptoms
- Bempedoic acid side effects include tendon rupture, increased uric acid levels, gout, and reduced glomerular filtration rate
- Should not be used with certain statins and fibrates due to drug interactions
Bempedoic Acid and Other Cholesterol-Lowering Treatments
- Can be used as an adjunct to statin and nonstatin therapies, producing an additional 16 to 26% reduction in LDL cholesterol levels
- Further reduction of cardiovascular events risk is still unclear, requiring more specific trials
- For statin-intolerant patients, data from the CLEAR Outcomes trial indicate bempedoic acid may reduce both LDL cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular events
Stroke, Myocardial Infarction, and Pulmonary Embolism after Bivalent Booster
- Introduction
- Bivalent mRNA vaccine targeting ancestral and omicron BA.4–BA.5 sublineages introduced in France in October 2022.
- Recommended for booster vaccination in vulnerable populations.
- Possible increased risk of ischemic stroke within 21 days after bivalent injection in persons 65 years or older.
- Study aims to assess risk of events after bivalent booster compared to monovalent booster.
- Study Design
- Population-based study using data from French National Health Data System linked to Covid-19 vaccination database.
- Participants: Persons 50 years or older who received booster dose between October 6 and November 9, 2022.
- 932,583 persons received bivalent vaccine, 121,362 received monovalent vaccine.
- Recipients followed for 21 days after vaccination.
- Risks of cardiovascular events estimated using propensity score-weighted Cox models.
- Results
- Total of 470,962 vaccine recipients (mean age: 72.6±10.4 years).
- 97,234 (20.6%) received monovalent vaccine, 373,728 (79.4%) received bivalent vaccine.
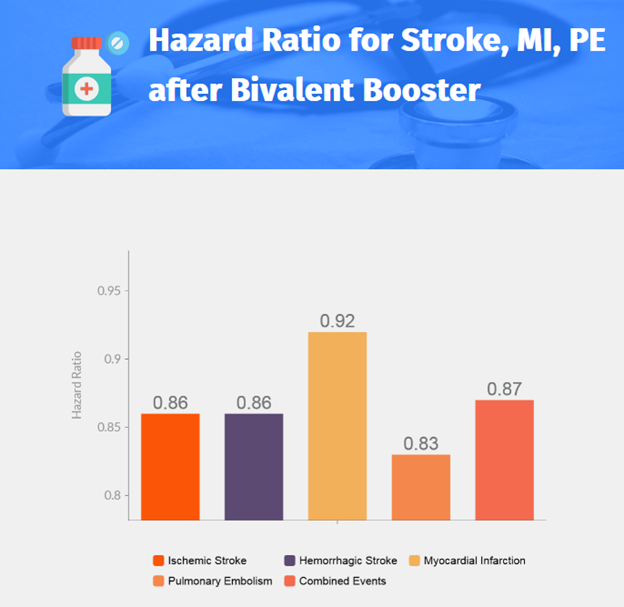
- No evidence of increased risk of cardiovascular events in bivalent vaccine recipients compared to monovalent vaccine recipients.
- Evaluated events: ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, and all four events combined.
- Conclusion
- Results provide reassurance regarding the continued use of the bivalent vaccine.
Erythema and Induration after Mpox (JYNNEOS) Vaccination Revisited
FDA Authorization of Vaccine
- In response to the 2022 outbreak of mpox (monkeypox).
- Dose-sparing intradermal administration of modified vaccinia Ankara vaccine (MVA-BN; trade name, JYNNEOS).
Trial details
- Sponsored by the National Institutes of Health.
- Investigated lyophilized and liquid formulations of MVA-BN vaccine.
- Compared subcutaneous administration of liquid formulation at standard dose with intradermal administration at one fifth the standard dose.
Trial results
- 167 participants in subcutaneous-administration group, 191 in intradermal-administration group.
- Geometric mean of peak neutralization titer: 49.5 for subcutaneous-administration and 59.5 for intradermal-administration.
- Response rate: 95.3% in subcutaneous-administration group, 94.5% in intradermal-administration group.
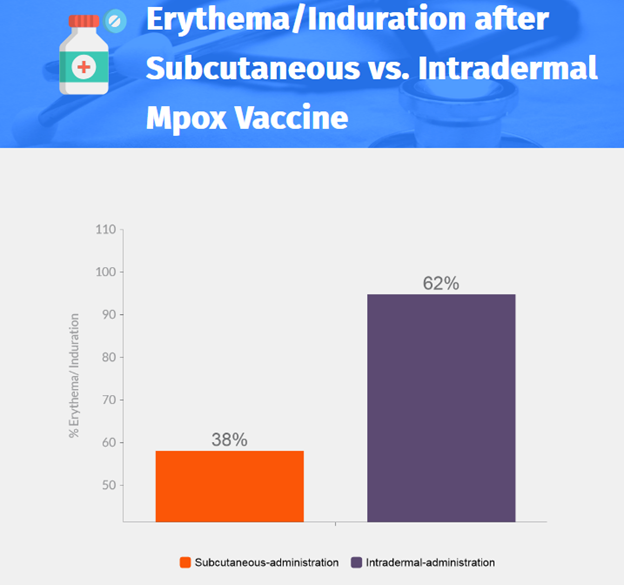
- Injection-site pain: 91.0% for subcutaneous-administration, 65.4% for intradermal-administration.
- Itchiness: 48.5% for subcutaneous-administration, 89.0% for intradermal-administration.
Local reactogenicity
- Moderate or severe reaction: 58.1% for subcutaneous-administration, 94.8% for intradermal-administration.
- Reactions monitored by CDC were consistent with prelicensure studies.
Reanalysis using FDA Toxicity Grading Scale
- Intradermal route deemed safe and not causing unacceptable local reactions.
- Higher incidence of moderate or severe erythema after second vaccine dose, but median duration of erythema was shorter in the intradermal-administration group.
- Intradermal route allows for 80% vaccine dose sparing compared to subcutaneous route.
- Adverse events considered acceptable for protection against mpox.
Luspatercept as Potential Treatment for Congenital Sideroblastic Anemia
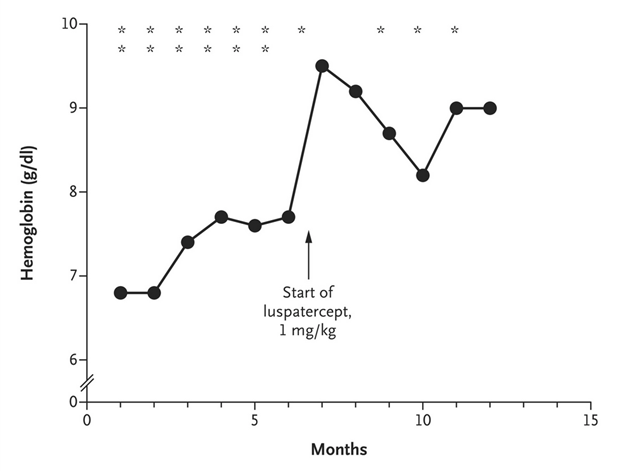
X-linked sideroblastic anemia
- Rare chronic anemia caused by missense mutations in ALAS2 gene
- Leads to ineffective erythropoiesis and anemia-related symptoms
- No disease-modifying treatment, except for hematopoietic allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Current treatment and issues
- Supportive therapy with pyridoxine supplementation and red cell transfusion
- Results in iron overload, affecting quality of life
Luspatercept as a potential treatment
- Binds TGF-β superfamily ligands, reducing SMAD2 and SMAD3 signaling
- Effective in low-to-intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia
Case report
- 51-year-old man with X-linked sideroblastic anemia and ALAS2 mutation
- Treated with luspatercept (1 mg/kg every 3 weeks)
- Substantial reduction in anemia-related symptoms and transfusion burden
- Hemoglobin increased by 30%, iron overload stabilized
Implications and future directions
- Luspatercept shows potential as a treatment option for X-linked sideroblastic anemia
- Clinical trials needed for this and other rare anemias with ineffective erythropoiesis
Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition in Advanced CKD
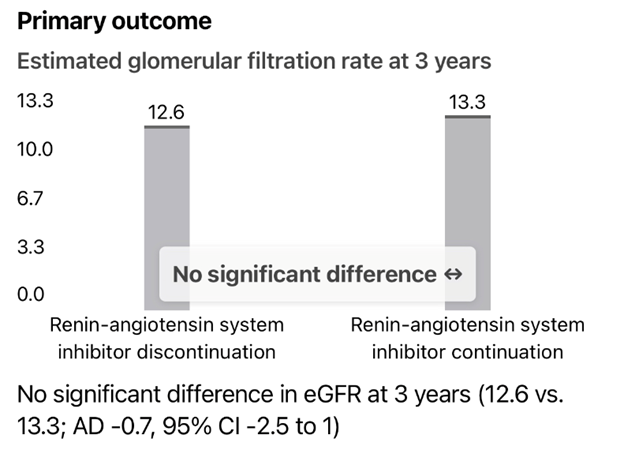
- Bhandari et al. study on ACE inhibitors and ARBs in advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Mechanisms of action for ACE inhibitors and ARBs
- ACE inhibitors: Block conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, affecting AT1 and AT2 receptors.
- ARBs: High selectivity for AT1 receptors, indirectly enhancing AT2 receptor activity.
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) components in the kidneys
- Dosage of RAS inhibitors should prevent pathophysiological RAS actions while maintaining homeostatic and regenerative functions.
Differentiating effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs
- ARBs may better inhibit RAS activity, which could be clinically important.
STOP-ACEi trial findings
- No significant difference in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at 3 years between patients who continued or discontinued RAS inhibitors.
- High levels of plasma renin activity may require adjusting the use or dose of natriuretic agents.
Comparing STOP-ACEi trial with an observational nationwide study
- Different follow-up durations, sample sizes, and patient characteristics.
- Similar outcomes regarding end-stage kidney disease and renal-replacement therapy at 3 years.
- Observational study showed more cardiovascular events and deaths in patients who discontinued RAS inhibitors.
Authors' response
- Ongoing analysis to assess outcomes based on the type of therapy (ACE inhibitor or ARB).
- Individualized care based on biomarker analysis needs further study.
- Extended follow-up unlikely to show the benefit of discontinuation based on eGFR findings.
Periprosthetic Joint Infection
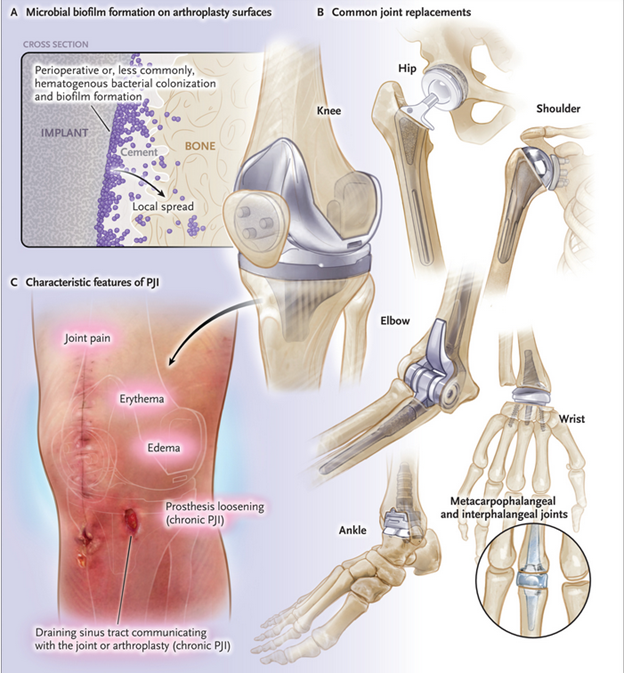
Patel's review on periprosthetic joint infection (PJI)
- Patel's review provides information on presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of PJI.
- Limited emphasis on targeted metagenomic sequencing (TMS) as a diagnostic tool.
Targeted metagenomic sequencing (TMS)
- Increased sensitivity of TMS compared to culture.
- PJIs are commonly polymicrobial, including viable but nonculturable microbes.
- TMS can identify opportunistic pathogens in culture-negative infections.
- Misrepresentation of TMS's clinical usefulness may limit its use in curative antimicrobial therapy.
Authors' response
- TMS detects potential pathogens in many culture-negative PJI cases.
- Cultures are positive in a significant percentage of PJI cases.
- Additional evidence needed before considering TMS for up-front diagnosis of PJI.
- Concerns: additional cost, potential identification of microorganisms of uncertain clinical significance, and overtreatment.
- Randomized, controlled trials needed to assess the use of up-front TMS.

Leave a Reply