Medicine Machines
- Ziad Obermeyer, an ER doctor, focuses on using machine learning in medicine for better decision-making and patient outcomes.
- His work includes creating algorithms to overcome biases and identifying biases in existing algorithms
- He discovered racial bias in a population health algorithm in 2019 and helped rectify it
- The conversation explores the potential of machine learning in end-of-life care and medicine, including overcoming the "garbage in, garbage out" issue with electronic health records
- EHRs contain a mix of objective data and potentially unreliable information.
- Garbage in, garbage out problem can be addressed by predicting the right thing.
- Algorithms can learn to distinguish between useful and non-useful data.
- Computational advances enable algorithms to focus on relevant information.
- Algorithmic bias occurs when the algorithm is instructed to predict the wrong thing.
- Issues arise when the algorithm predicts a proxy measure rather than the actual outcome of interest.
- Conversation discusses algorithmic bias, applicability in emergency departments, and aiding cardiologists in identifying patients that do or do not need testing
- Algorithm built using hospital data to predict positive catheterization results.
- Algorithm learned to predict who would require a stent and who wouldn't.
- Algorithm deployed on new patients and compared to doctor's decisions and patient outcomes.
- Two-thirds of high-cost tests were predicted negative by the algorithm, confirming overtesting.
- Half of high-risk patients were not tested by doctors, suggesting undertesting.
- Undertesting of high-risk patients leads to higher rates of adverse events.
- High-risk patient outcomes differ depending on testing tendencies of providers.
- Study results being used in collaboration with a large health care system (Providence).
Is medicine ready for AI?
- Dr. Hightower is excited about AI's potential to democratize diabetic retinopathy screening and improve clinical documentation through voice recognition. However, she is also concerned about AI bias and founded a company called Equality AI to mitigate it.
- Dr. Kohane believes that AI can help address physician burnout by taking over administrative tasks and providing support to physician assistants and nurse practitioners. He also stresses the importance of measuring AI's effectiveness and avoiding a false sense of security.
- Both doctors agree that AI should be used as decision support, not a decision maker, and that it should complement human intuition and common sense in patient interactions. They believe that by combining AI's strengths with human strengths, the best outcomes can be achieved.
Palmar Erythema of Pregnancy
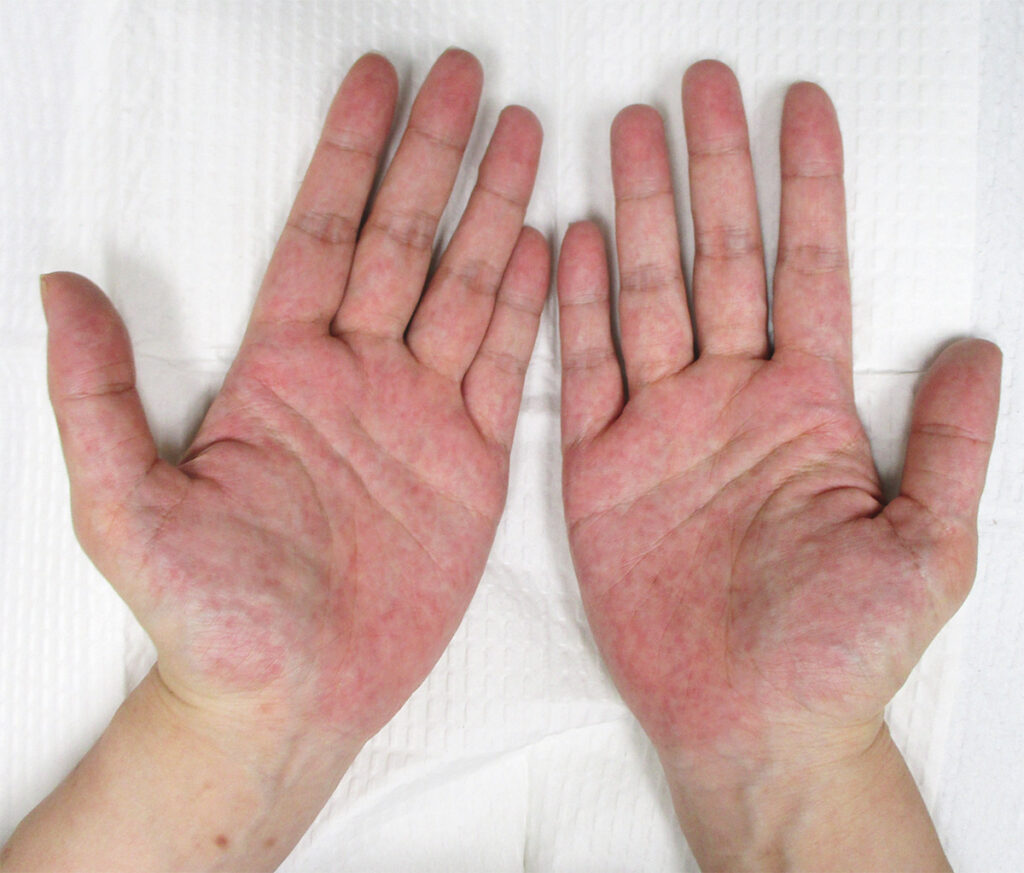
- 33yo woman with gestational diabetes
- 35 weeks' gestation
- Redness on both palms
- No pain, pruritus, or rashes elsewhere
- Skin changes began in second trimester
- Topical glucocorticoids didn't help
- Diagnosis: palmar erythema of pregnancy
- Physiologic vascular skin change
- Erythema may be diffuse and blotchy or limited
- Possible itching, tingling, or burning
- No specific treatment required
- Resolves within 2 weeks to 2 months after birth
- Erythema decreased 1 week after delivery
- Fully resolved by 2 months postpartum
Ensuring Public Trust in an Empowered FDA
- FDA granted accelerated approval to lecanemab (Leqembi) for Alzheimer's treatment on January 6, 2023.
- Accelerated approval program enables earlier drug approvals for serious conditions and unmet medical needs.
- Controversy surrounds recent FDA authorizations under accelerated approval program.
- Questions arise about surrogate markers, postmarketing requirements, and the FDA's ability to withdraw products.
- Lecanemab approval based on a single trial, despite objections from FDA biostatisticians.
- FDA taking an empowered stance in the use of accelerated approval.
- Food and Drug Omnibus Reform Act includes FDA-supported modifications to the accelerated approval program.
- FDA could consider additional steps to better support clinicians, patients, and caregivers.
- Clinicians face challenges in guiding patients with uncertain drug safety and efficacy.
Why Diverse Clinical Trial Participation Matters
- Marginalized racial and ethnic groups, women, and other historically disenfranchised populations underrepresented in clinical trials.
- Goals of increasing diversity: earning and building trust, promoting fairness, and generating biomedical knowledge.
- Earning trust: inclusive enrollment practices can increase patients' interest and confidence in effective new treatments.
- Promoting fairness: remove obstacles to participation and ensure burdens of participation are shared broadly and equitably.
- Advancing biomedical knowledge: diverse trials may improve generalizability, produce new insights, and yield targeted therapeutic strategies.
- Diversifying trial participation may speed innovation by enabling more rapid accrual.
- Central goals: building trust among underserved communities and treating potential participants fairly.
- Creating an evidence base built on studies with diverse populations is crucial to mitigate health outcome inequalities.
A Quixotic Quest for Independence — Benefits, Risks, and the Human Heart
- A neurologist shares his perspective growing up with a brother, David, with cerebral palsy
- David had damaged muscles and cerebral palsy from a forceps delivery at birth
- Parents focused on helping David become independent, teaching him life skills
- David achieved a bachelor's degree, swam, drove, and supported himself
- Medical community changed over time, leading to fragmented care for David
- David developed depression and psychosis, exacerbated by medication interactions
- Author (a neurologist) intervened with medications, but felt guilt for David's struggles
- David married, but the relationship was unhealthy and worsened his depression
- Family helped David throughout his life, but faced challenges with his desire for normalcy
- Author wonders if different choices could have been made, but ultimately feels the focus on independence was valuable
Trial of Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Ischemic Strokes
- Study: Prospective, randomized, open-label, adaptive, international trial
- Participants: Patients with large ischemic-core strokes due to occlusion of internal carotid artery or middle cerebral artery
- Treatment: Endovascular thrombectomy within 24 hours of onset
- Control: Medical care alone
- Primary outcome: Modified Rankin scale score at 90 days
- Secondary outcome: Functional independence
- Results:
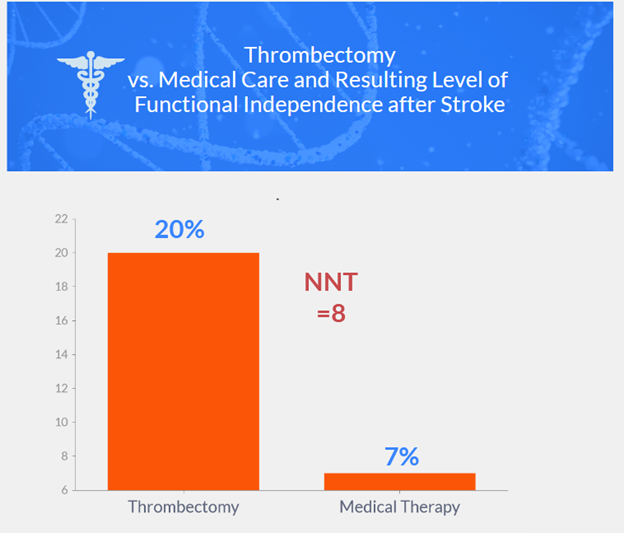
- Thrombectomy group had better functional outcomes (generalized odds ratio 1.51, p<0.001)
- 20% in thrombectomy group vs. 7% in medical care group achieved functional independence (relative risk 2.97)
- Mortality rates similar in both groups
- Vascular complications in thrombectomy group: arterial access-site complications (5 patients), dissection (10 patients), cerebral-vessel perforation (7 patients), transient vasospasm (11 patients)
- Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage: 1 patient in thrombectomy group, 2 patients in medical care group
- Thrombectomy group had better functional outcomes (generalized odds ratio 1.51, p<0.001)
- Conclusion: Endovascular thrombectomy resulted in better functional outcomes but with vascular complications; cerebral hemorrhages infrequent in both groups
Trial of Endovascular Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Large Infarct
- Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized trial in China
- Patients with acute large-vessel occlusion and specific infarct-core volume
- Randomly assigned 1:1 to endovascular therapy + medical management or medical management alone
- Primary outcome: modified Rankin scale score at 90 days
- Primary objective: determine shift in modified Rankin scale scores at 90 days between groups
- Secondary outcomes: modified Rankin scale scores of 0-2 and 0-3
- Primary safety outcome: symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage within 48 hours after randomization
- 456 patients enrolled: 231 in endovascular-therapy group, 225 in medical-management group
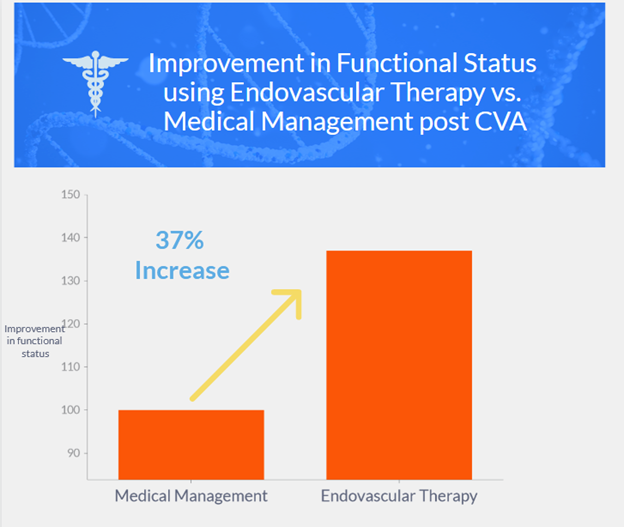
- Trial stopped early due to endovascular therapy efficacy
- At 90 days, endovascular therapy had better outcomes than medical management alone (generalized odds ratio 1.37, P=0.004)
- More intracranial hemorrhages in endovascular-therapy group
GD2-CART01 for Relapsed or Refractory High-Risk Neuroblastoma
- Study focused on immunotherapy with GD2-targeting CAR T cells for high-risk neuroblastoma patients
- Phase 1-2 clinical trial, enrolling patients aged 1-25 with relapsed or refractory high-risk neuroblastoma
- Tested autologous, third-generation GD2-CAR T cells with inducible caspase 9 suicide gene (GD2-CART01)
- 27 children enrolled, heavily pretreated neuroblastoma (refractory, relapsed, and complete response cases)
- Three dose levels tested, no dose-limiting toxic effects; recommended dose for phase 2: 10×106 CAR-positive T cells/kg
- Cytokine release syndrome in 20 of 27 patients (74%), mild in 19 of 20 (95%)
- Suicide gene activated in 1 patient, rapid elimination of GD2-CART01
- CAR T cells expanded in vivo, detectable in peripheral blood up to 30 months (median persistence: 3 months)
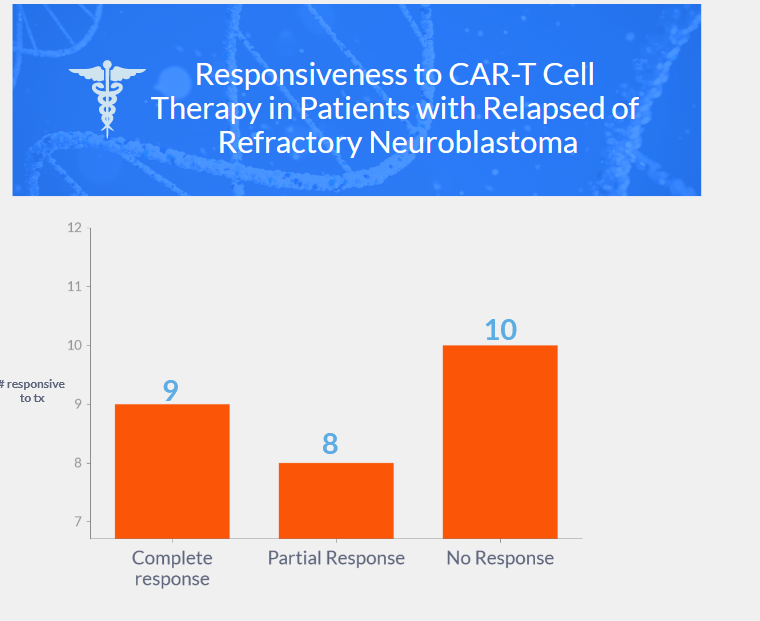
- Overall response: 63% (9 complete responses, 8 partial responses)
- Recommended dose patients: 3-year overall survival 60%, event-free survival 36%
- GD2-CART01 feasible and safe for high-risk neuroblastoma treatment, sustained antitumor effect
Postexposure Doxycycline to Prevent Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections
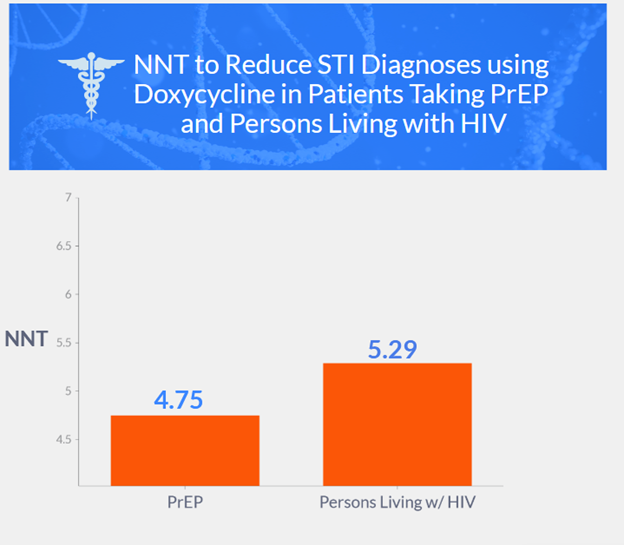
- Open-label, randomized study conducted on MSM (men who have sex with men) and transgender women taking pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against HIV or living with HIV and had a recent history of gonorrhea, chlamydia, or syphilis.
- Participants were randomly assigned to take 200 mg of doxycycline within 72 hours after condomless sex (doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis) or receive standard care without doxycycline.
- STI testing was performed quarterly, and the primary endpoint was the incidence of at least one STI per follow-up quarter.
- Results show a significant reduction in STI incidence in the doxycycline group compared to the standard-care group in both the PrEP cohort and the persons living with HIV infection (PLWH) cohort.
- Doxy-PEP decreased incident gonorrhea, chlamydia, and early syphilis by two-thirds among MSM and transgender women with a bacterial STI in the previous year
- Doxy-PEP study showed a 55% reduction in incident gonorrhea, including pharyngeal gonorrhea
- Effectiveness against chlamydia: 88% in PrEP cohort, 74% in PLWH cohort
- Reduction in syphilis observed in PrEP cohort and trend towards reduction in PLWH cohort
- S. aureus carriage 40% lower in doxycycline groups than in standard-care groups at month 12
- Tetracycline-resistant gonorrhea occurred in 5 of 13 participants in the doxycycline groups and 2 of 16 in the standard-care groups
- Study limitations: measuring adherence to doxy-PEP, limited tetracycline susceptibility results, low enrollment of transgender women, conducted in two West Coast cities.
- Conclusion: The combined incidence of gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis was lower by two-thirds with doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis than with standard care, supporting its use among MSM with recent bacterial STIs
Primary Budd–Chiari Syndrome
- Primary Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) is a rare and fatal disease characterized by hepatic venous outflow tract obstruction due to thrombosis or primary disease of the venous wall.
- BCS can be caused by an underlying disorder such as hereditary or acquired hypercoagulable state, and myeloproliferative neoplasm is the most common underlying condition.
- Chronic hepatic venous obstruction in BCS leads to the development of hepatic fibrosis, ascites formation, and portal hypertension.
- Testing for driver somatic mutations in genes encoding JAK2, CALR, and MPL is important for suspected BCS cases.
- Other prothrombotic disorders associated with BCS include factor V Leiden, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, and antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Tests for inherited protein C, protein S, and antithrombin deficiencies must also be performed.
- Oral contraceptive use, recent pregnancy, and systemic diseases may increase the risk of BCS.
- Improved access to genetic tools may reveal the real contribution of inherited deficiencies in natural anticoagulant proteins to the development of BCS.
- Clinical manifestations of Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) are varied and non-specific, and the absence of clinical manifestations is not rare
Diagnosis
- Laboratory abnormalities in BCS include altered liver function tests and blood-cell counts indicating hypersplenism.
- BCS can be diagnosed by identifying obstruction of the hepatic venous system on imaging
- Doppler ultrasonography, CT, or MRI can be used to diagnose BCS
Prognosis
- BCS is associated with high mortality (>80% at 3 years)
- Several prognostic scores have been developed to classify the severity of BCS
- An alanine aminotransferase level that is 5 or more times the upper limit of the normal range at presentation and that does not decrease rapidly in the next few days is associated with poor prognosis
Treatment
- Treatment options for BCS include anticoagulation, restoration of hepatic venous outflow, and treatment of the underlying prothrombotic disorder
- Referral to tertiary centers with multidisciplinary teams is recommended for managing BCS.
- Liver transplantation is the last option for patients in whom other treatments have failed.
Acute Ocular Toxoplasmosis
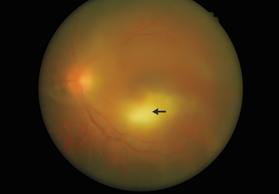
- A 49-year-old man presented with blurry vision and glare in his left eye.
- Ophthalmologic examination showed visual acuity of 20/200 in the left eye and mild granulomatous uveitis.
- Ocular examination revealed focal chorioretinitis and moderate vitreous inflammation in the left eye only.
- The diagnosis was acute ocular toxoplasmosis, with the patient reporting contact with his pet dog.
- Ocular toxoplasmosis is the most common infectious cause of posterior uveitis and is a clinical diagnosis.
- Treatment with oral antimicrobial therapy and systemic glucocorticoid agents was initiated.
- At follow-up, the vitreous inflammation of the left eye had abated, but visual acuity remained 20/200.
An Alternate Explanation
- The patient, a 48-year-old man with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease, presented with numbness, tingling, and violaceous discoloration of the fingers and toes, reduced light-touch sensation in a glove-and-stocking distribution, palpable peripheral pulses, and an ankle-brachial index of 1.2 on both sides.
- The patient was later admitted to a hospital with acute dyspnea, hypotension, and kidney injury
- Ultrasonography revealed a deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Warfarin-induced skin necrosis was suspected, but other possibilities include an underlying severe hypercoagulable state or vasculitis.
- Despite treatment with intravenous antibiotics, urgent source control necessitated a left below-knee amputation
- The patient was discharged home with a plan for wound care and a 3-month course of apixaban, with follow-up arranged with his primary care physician and a vascular medicine specialist.
- Whole-genome sequencing identified a missense mutation in NT5E that leads to a deficiency of CD73, resulting in a diagnosis of arterial calcification due to deficiency of CD73 (ACDC).
- The patient was treated with wound care and infusions of the calcium chelator sodium thiosulfate during hemodialysis, which led to the healing of all his open wounds and the salvage of his nonnecrotic digits
- The patient continued to receive infusions of sodium thiosulfate during each hemodialysis session, and a year later, all wounds had healed, and no new wounds had appeared.
- This case highlights the importance of considering nonatherosclerotic mechanisms of vascular calcification and early administration of agents that affect calcium metabolism to prevent rapid progression of vascular disease.
Improved Prospects for Thrombectomy in Large Ischemic Stroke
- Mechanical endovascular thrombectomy is highly effective for small-to-moderate acute ischemic strokes; 70-80% recanalization rates
- Number needed to treat: 2.3 for preventing disability in stroke patients
- Treatment guidelines: thrombectomy for ischemic-core volumes <50 ml
- Large strokes: ASPECTS values ≤5 or ischemic-core volume ≥50 ml
- Modified Rankin scale: assesses disability on a scale of 0 (no disability) to 6 (death)
Clinical trial data
- Japanese trial: thrombectomy improved functional outcomes in large strokes
- SELECT2 recruitment stopped due to positive results of the Japanese trial.
- Primary outcome favored thrombectomy (modified Rankin scale score).
- Thrombectomy group had more than double the number of patients with functional independence and independent ambulation (secondary outcomes).
- Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage infrequent and similar in both groups.
- Death incidence similar in both groups, but neurologic worsening more frequent in thrombectomy group, associated with worse outcomes.
- SELECT2 trial: thrombectomy favored; more functional independence and independent ambulation
- ANGEL-ASPECT trial: thrombectomy showed "good outcomes" in 47.0% of patients
- Benefits consistent across age, neurologic deficit, imaging, time of treatment, and geography
- Trials suggest thrombectomy for large strokes (ASPECTS 3-5 or ischemic-core volume ≥50 ml)
- Improved chance of independent walking and daily activity performance, but with increased risks
CAR T Cells for Neuroblastoma
- Neuroblastoma: aggressive pediatric cancer, most common extracranial cancer in children
- Poor prognosis, burdensome treatment
- Tx for high-risk patients: induction therapy, consolidative therapy, maintenance treatment
- Recurrence rates high, salvage therapies limited
- Del Bufalo et al. study: CAR T-cell therapy for high-risk neuroblastoma
- GD2 as a target: low expression in healthy tissue, elevated in tumor types
- CAR T cells: genetically modified T cells, express CAR for tumor-associated antigens
- GD2-CART01 features: three stimulatory domains, safety switch (iC9)
- Safety switch mechanism: rimiducid activates iC9, inducing apoptosis in CAR T cells
- Cytokine release syndrome: Common side effect- fever, hypotension, hypoxia
- Treated with tocilizumab and glucocorticoids
- Next steps: investigate resistance mechanisms, metabolic fitness of CAR T cells, potential combination therapies
Understanding the Genetic Risk of IDH-Mutant Glioma
- Adult low-grade gliomas: diffusely infiltrating primary brain tumors
- Defined by somatic variants in genes encoding IDH1 (chromosome 2) and IDH2 (chromosome 15)
- IDH mutations disrupt cellular metabolism, induce DNA methylation, change chromatin structure
- IDH-mutant gliomas: astrocytoma (grades 2-4) and oligodendroglioma (grades 2-3)
- Low-grade gliomas: 25% of ~17,000 infiltrating gliomas diagnosed annually in the US
- Limited targetable driver mutations for precision oncology
- Genomewide association studies: 19 loci associated with low-grade glioma risk
- Ionizing radiation: only established and modifiable risk factor for low-grade glioma
- Chromosome 8q24 polymorphism: linked to IDH-mutant low-grade glioma risk
- Yanchus et al.: rs55705857 causes low-grade glioma risk via long-distance MYC up-regulation
- rs55705857 functions as a lineage-specific embryonic enhancer
- rs55705857-G risk allele disrupts binding of OCT2 and OCT4, increasing MYC activation
- IDH mutations may affect tumorigenesis by facilitating MYC activation
- rs55705857-G not yet translated into useful risk-prediction models
- Neural features predisposing to low-grade glioma may be established in utero
- Yanchus et al.'s study provides integrated framework for etiologic research on low-grade glioma
Viral Lineages in the 2022 RSV Surge in the United States
- Unusually early surge of RSV disease in the US in autumn 2022
- Sequenced RSV genomes from symptomatic patients in the greater Boston area
- 54 near-complete and 23 partial RSV genomes obtained
- Viral respiratory coinfections found in some specimens
- Surge driven by multiple lineages of RSV-A (91%) and RSV-B (9%)
- RSV-A genomes belonged to at least 10 distinct clades
- Genetic divergence consistent with estimated clock rate, not accelerated evolution
- 2022 RSV surge not caused by a single, highly transmissible lineage
- Nonviral factors, such as changes in population immunity and Covid-19 interventions, may have affected the surge
Cambridge Prophylactic Protocol, Retinal Detachment, and Stickler Syndrome
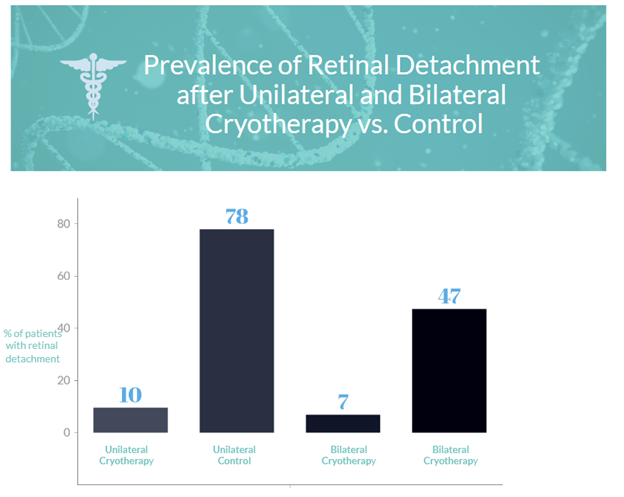
- Stickler syndromes are inherited conditions affecting 1 in 7500 live births, with type 1 Stickler syndrome being the most common cause of childhood retinal detachment.
- The Cambridge Prophylactic Cryotherapy Protocol aims to prevent retinal detachment related to giant retinal tears in type 1 Stickler syndrome patients.
- 778 patients with type 1 Stickler syndrome were included in the study, divided into unilateral and bilateral cryotherapy groups and control groups.
- Prophylaxis failure (retinal detachment) occurred in 7.4% of patients (39 of 529) with a mean time of 7.4±9.8 years from treatment to failure.
- The prevalence of second-eye retinal detachment was significantly lower in the cryotherapy groups compared to control groups after patient matching to control for confounders
- Short-term side effects of prophylaxis were minor and mean visual acuity was unaffected by the procedure.
- The study suggests that the Cambridge Prophylactic Cryotherapy Protocol reduces the risk of retinal detachment in type 1 Stickler syndrome patients, but acknowledges the limitations of a retrospective study.
Progression of Atrial Fibrillation after Cryoablation
- Andrade et al. found that cryoballoon ablation as an initial strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation was associated with a lower incidence of persistent atrial fibrillation and lower burden of arrhythmia compared to antiarrhythmic drugs during 3 years of follow-up.
- The EARLY-AF and STOP AF First 3 trials also suggested cryoballoon ablation as a superior initial therapy for preventing atrial arrhythmia recurrence in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
- The follow-up study of EARLY-AF trial provides longer-term evidence on the clinical benefits of early catheter ablation as a rhythm-control strategy, and it may limit the progression of atrial fibrillation and improve clinical outcomes.
Chlorthalidone vs. Hydrochlorothiazide for Hypertension–Cardiovascular Events
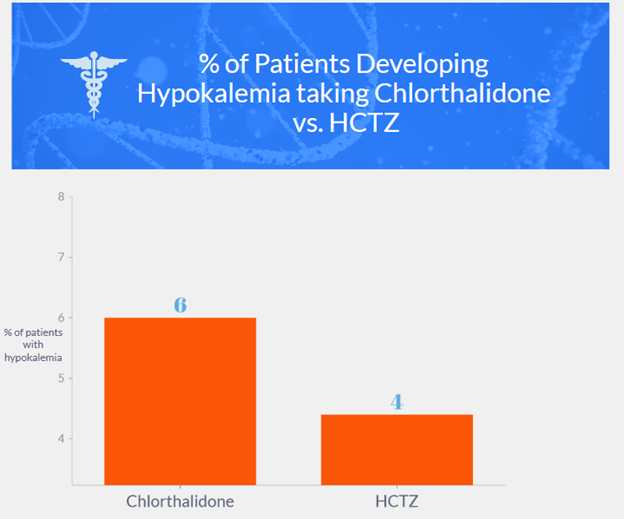
- A comparison was made between chlorthalidone and hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension-cardiovascular events.
- Chlorthalidone had a higher incidence of hypokalemia compared to hydrochlorothiazide.
- In the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program trial, participants with hypokalemia had similar cardiovascular risks to those in the placebo group, which abolished all cardiovascular benefits of chlorthalidone therapy.
- The Diuretic Comparison Project used lower doses of chlorthalidone and involved participants with controlled blood pressure at baseline, making it unlikely to see differences in blood pressure lowering between the two groups.
- Participants with a history of myocardial infarction appeared to benefit more from chlorthalidone, possibly due to higher doses.
- The use of low doses of hydrochlorothiazide in the trial could have influenced the results, and it is unclear if higher doses would have made a difference.
Evidence over Politics — U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
- Combining antiarrhythmic drug therapy with catheter ablation may decrease the recurrence of atrial tachyarrhythmia and should be considered preferable in daily practice.
- Cryoablation results in significant reductions in arrhythmia recurrence and improvements in quality of life compared to initial antiarrhythmic drug therapy.
- Cryoballoon ablation may result in less healthcare utilization and hospitalizations than antiarrhythmic drugs, but the duration of follow-up necessary to detect a difference in mortality may be much longer.
- Combining catheter ablation with antiarrhythmic drugs can be considered as complementary therapies, and previously ineffective antiarrhythmic drugs may become effective in controlling arrhythmia recurrence after an ablation procedure.
- Lerner and Curtiss-Rowlands defend the USPSTF from critics but the correspondents point out flaws in the process.
- Evidence reviews are done by researchers from Evidence-based Practice Centers (EPCs).
- Suggestions for reforms include: making public comments public, using new authors for each iteration of a topic, using specified criteria to reduce subjectivity, and including topic expertise.
- There is a trade-off between setting the bar too high or too low for evidence of the value of a screening test before it is recommended.
- The USPSTF does not exclude intervening data but evaluates it on its merits and reassessments are done by a largely new slate of evaluators.
- The USPSTF has published numerous articles on the criteria it uses to make its decisions.
- Beckman’s call for making the evaluation process as transparent as possible is agreed upon.

Leave a Reply