CLOT
Is LMWH superior to Warfarin for the prevention of recurrent VTE in patients with cancer?
Study design

Population
- 676 patients (348 female, 328 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients with cancer who had acute, symptomatic proximal DVT, pulmonary embolism, or both
- Key exclusion criteria: weight ≤ 40 kg, ECOG performance status score of 3 or 4, receipt of OAC therapy, serious bleeding within the previous two weeks, high risk of serious bleeding, contraindications to heparin therapy, or pregnancy
Interventions
- N=338 subcutaneous dalteparin (200 IU of dalteparin per kilogram once daily for the first month and approximately 150 IU per kilogram for the remaining 5 months)
- N=338 oral anticoagulation (dalteparin at a dose of 200 IU per kilogram of body weight SC once daily for 5-7 days and vitamin K antagonist for 6 months)
Primary outcome
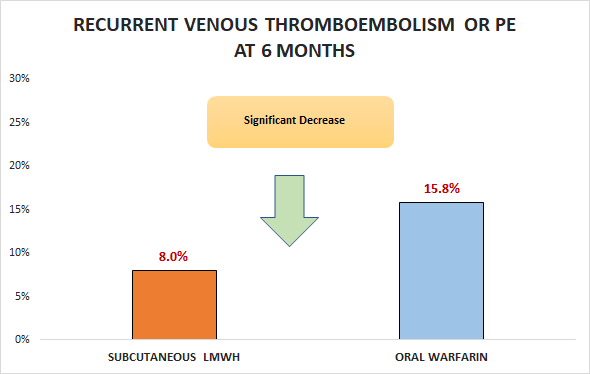
Secondary outcomes
No significant difference in death (39% vs. 41%; RR 0.95, 95% CI-1.94 to 3.84)
Safety outcomes
No significant difference in rate of major bleeding (6% vs. 4%) or any bleeding (14% vs. 19%).
Conclusion
In patients with cancer who had acute, symptomatic proximal DVT, pulmonary embolism, or both, subcutaneous LMWH was superior to oral anticoagulation with respect to recurrent VTE at 6 months.
