AVOID
What is the role of supplemental oxygen therapy in patients with STEMI?
Study design

Population
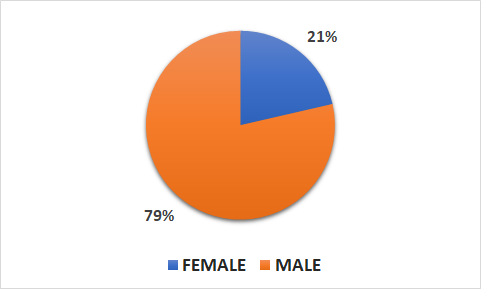
- 638 patients (93 female, 348 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients with STEM diagnosed on paramedic 12-lead ECG
- Key exclusion criteria: oxygen saturation < 94% measured on pulse oximeter, bronchospasm requiring nebulized salbutamol therapy with oxygen, oxygen administration before randomization, or altered conscious state
Interventions
- N=318 routine supplemental oxygen (via face mask at
8 L min) - N=320 restricted supplemental oxygen (no oxygen unless oxygen saturation < 94%, in which case oxygen was administered via nasal cannula (4 L/min) or face mask (8 L/min) to achieve an oxygen saturation of 94%)
Primary outcome
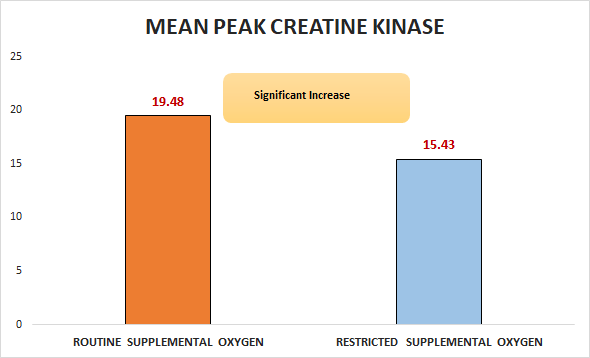
Secondary outcomes
- Significant increase in recurrent myocardial infarction
(5.5% vs. 0.9%; RR 6.1, 95% CI 1.75 to 10.45) - No significant difference in geometric mean peak cTl in patients with confirmed STEMI (57.4 ug/L vs. 48 ug/L; RR 1.2, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.56)
Safety outcomes
No significant differences in mortality at hospital discharge (1.8% vs. 4.5%, p=0.11).
Conclusion
In patients with STEMI diagnosed on paramedic 12-lead ECG, routine supplemental oxygen was inferior to restricted supplemental oxygen with respect to mean peak CK.
