ARDSNet
Is ventilation with lower tidal volumes superior to traditional tidal volume in patients with ARDS?
Study design

Population
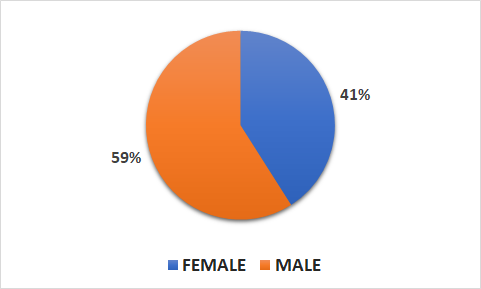
- 861 patients (349 female, 512 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients with ARDS and acute lung injury
- Key exclusion criteria: younger than 18 years of age; pregnancy; increased ICP, neuromuscular disease that could impair spontaneous breathing, sickle cell disease, or severe chronic respiratory disease; bone marrow or lung transplantation; chronic liver disease
Interventions
- N=432 ventilation with lower tidal volumes (initial tidal volume of 6 mL/kg of predicted body weight and a plateau pressure ≤ 30 cmH20)
- N=429 traditional tidal volume (initial tidal volume of 12 mL/kg of predicted body weight and plateau pressure
≤ 50 cmH20)
Primary outcome
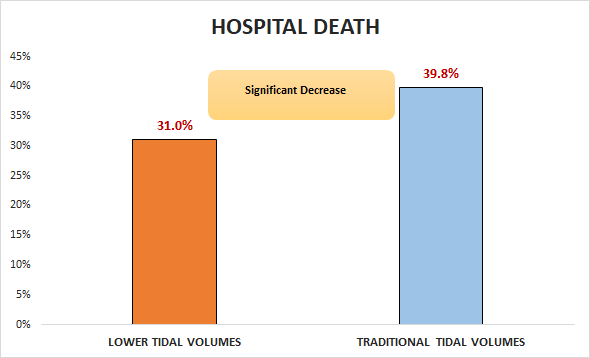
Secondary outcomes
Significant increase in ventilator-free days at 28 days (12 days vs. 10 days; ARD 2, 95% CI 0.55 to 3.45)
Conclusion
In patients with ARDS and acute lung injury, ventilation with lower tidal volumes were superior to traditional tidal volume with respect to hospital death.
