ADVANCE
What is the role of intensive glucose control in patients with T2DM?
Study design
Population
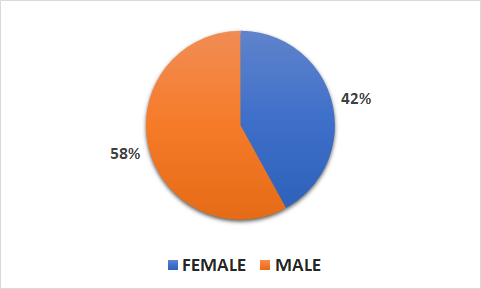
- 11140 patients (4733 female, 6407 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients with T2DM
- Key exclusion criteria: a definite indication for, or contraindication to, any of the study treatments or a definite indication for long-term insulin therapy at the time of study entry
Interventions
- N=5571 intensive glucose control (using gliclazide, modified release 30-120 mg daily, and other drugs, targeting glycated Hgb value < 6.5%)
- N=5569 standard glucose control (target glycated Hgb levels defined on the basis of local guidelines
Primary outcome
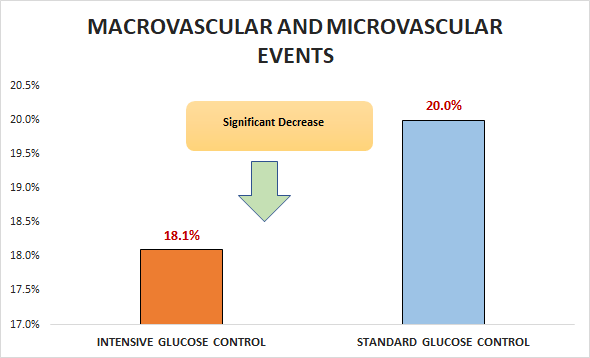
Significant decrease in macrovascular and microvascular events (18.1% vs. 20%; HR 0.9, 95% CI 0.82 to 0.98)
Secondary outcomes
- Significant decrease in major microvascular events
- (9.4% vS. 10.9%; HR 0.86, 95% CI 0.77 to 0.97)
- Significant decrease in nephropathy (4.1% vs. 5.2%; HR 0.79, 95% CI 0.66 to 0.93)
- No significant difference in death from any cause (8.9% vs. 9.6%; HR 0.93, 95% CI 0.83 to 1.06)
Safety outcomes
- No significant difference in RT or death from renal causes.
- Significant difference in severe hypoglycemia (2.7% VS. 1.5%).
Conclusion
In patients with T2DM, intensive glucose control was superior to standard glucose control with respect to macrovascular and microvascular events.
