ACCORD-BP
What is the effect of intensive BP control in patients with T2DM mellitus at high risk for cardiovascular events?
Study design

Population
- 4733 patients (2258 female, 2475 male)
- Inclusion criteria: patients with T2DM at high risk for cardiovascular events
- Key exclusion criteria: BMI > 45, a serum creatinine level > 1.5 mg/dL (132.6 mcmol/L), and other serious illness
Interventions
- N=2362 intensive BP control (targeting a systolic pressure of <120 mmHg)
- N=2371 standard BP control (targeting a systolic pressure of < 140 mmHg)
Primary outcome
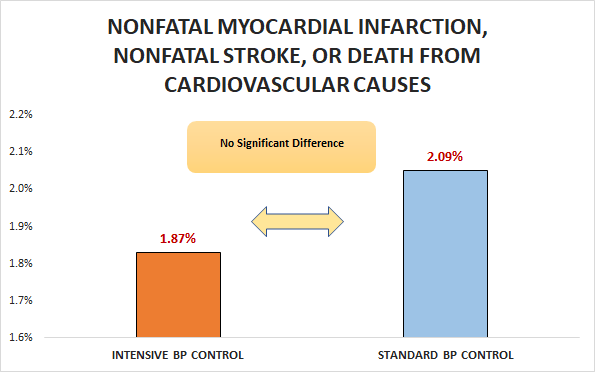
No significant difference in nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes (1.87% vs. 2.09%; HR 0.88, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.06)
Secondary outcomes
- No significant difference in annual death from any cause (1.28% vs. 1.19%; HR 1.07, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.35)
- Significant decrease in stroke at 1 year (0.32% VS. 0.53%; HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.39 to 0.89)
Safety outcomes
Significant differences in serious adverse events attributed to antihypertensive treatment (3.3% VS. 1.3%, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In patients with T2DM at high risk for cardiovascular events, intensive BP control was not superior to standard BP control with respect to nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes.
