ACCORD
What is the role of intensive glycemic control therapy in high-risk patients with T2DM?
Study design

Population
Characteristics of study participants (N= 10251)
• Inclusion criteria: patients with T2DM who had either established cardiovascular disease or additional cardiovascular risk factors
• Key exclusion criteria: frequent or recent serious hypoglycemic events, unwillingness to do home glucose monitoring or inject insulin, a body-mass index > 45, a serum creatinine level > 1.5 mg/dL (133 umol/L), or other serious illness Interventions
• N=5128 intensive glycemic control (targeting an HbA1C
< 6.0%)
• N=5123 standard glycemic control (targeting an HbA1C
7.0-7.9%)
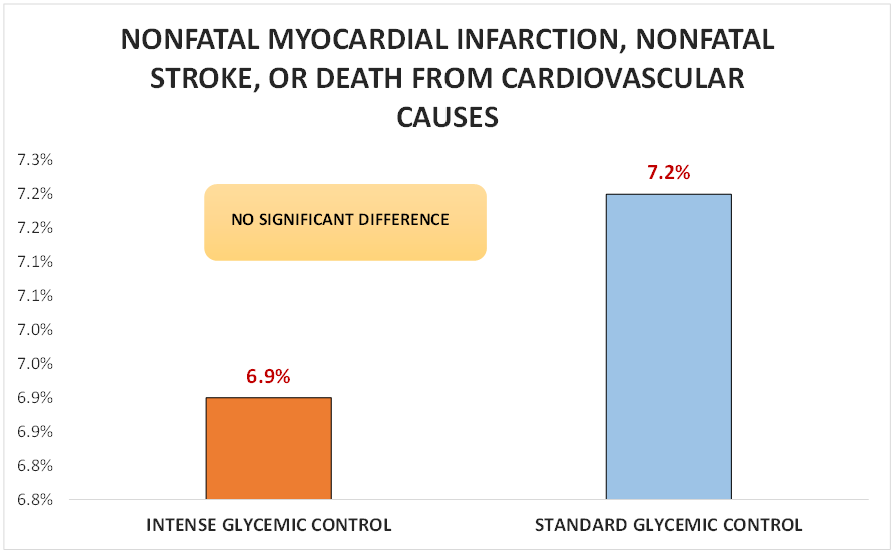
Primary outcome
Secondary outcomes
Significant increase in the rate of death at a mean follow-up of 3.5 years (5% vs. 4%; HR 1.22, 95% Cl 1.01 to 1.46)
Safety outcomes
Significant differences in hypoglycemia requiring assistance (16.2% Vs. 5.1%, p < 0.001) and weight gain > 10 kg (27.8% VS. 14.1%, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In patients with T2DM who had either established cardiovascular disease or additional cardiovascular risk factors, intensive glycemic control was not superior to standard glycemic control with respect to nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes.
