Combined CHA₂DS₂-VASc and HAS-BLED Calculator
CHA₂DS₂-VASc Score for Atrial Fibrillation Stroke Risk
HAS-BLED Score for Major Bleeding Risk
Background
- Ectopic atrial rhythm originating from abnormal foci near pulmonary veins
- Variable AV nodal conduction and ventricular rate (75-125 BPM)
- Classification: Paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent
- Risk factors: Age > 80, hypertension (HTN), coronary artery disease (CAD), atrial abnormalities, hyperthyroidism
- Triggers: Alcohol (EtOH), increased catecholamines (infection, surgery, pain)
- Symptoms: Asymptomatic or symptomatic (palpitations, presyncope, dyspnea)
Complications of Atrial Fibrillation
- Tachyarrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy: Dilated cardiomyopathy from prolonged tachycardia
- Embolic events: Stroke, mesenteric ischemia, limb ischemia, etc.
Diagnosis
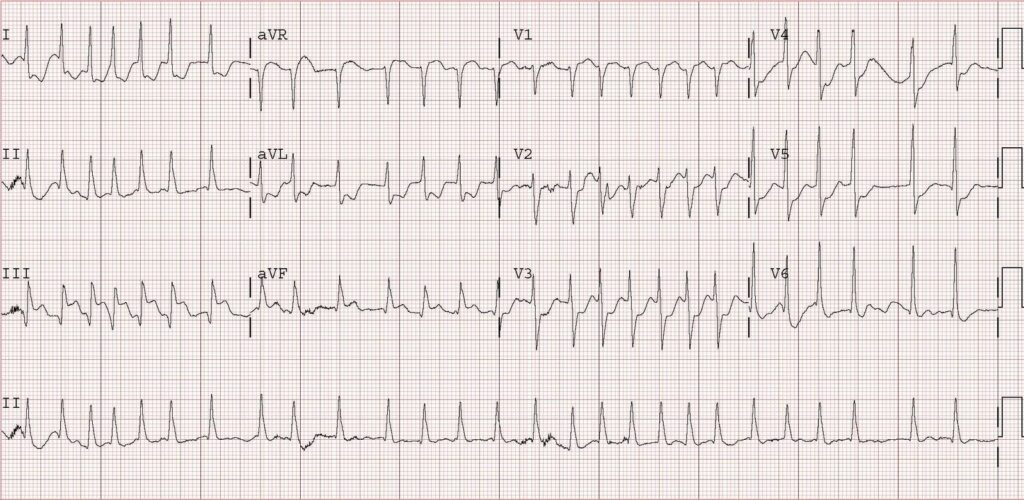
- Irregularly irregular rhythm on ECG
- Absence of distinct P waves
Management of New Onset Atrial Fibrillation
Step 1: Rate control (if necessary)
- Beta-blocker or calcium channel blocker (CCB)
- Goal: HR 110-120 BPM
- Rate control with metoprolol 5 mg IV q5 min x3 prn, then chase with PO metoprolol when rates stabilized. Target HR <110.
- Order TSH, lipid panel, A1c.
Step 2: Cardioversion (if still in AF after rate control)
- Preferred method: DC electrical cardioversion
- Drug options: Flecainide, propafenone, or ibutilide
- Anticoagulation required for at least 3 weeks or AF developed within the last 48 hr
Step 3: If in RVR: IV beta-blockers, CCB, Digoxin, or amiodarone
Step 4: Chronic therapy
Chronic Therapy
Rate Control
- Goal HR: < 85 BPM (symptomatic), < 110 BPM (asymptomatic)
- Drug choice: Beta-blocker (e.g., metoprolol), alternative options: CCB, digoxin
Rhythm Control
- Indication: < 65 years old, symptomatic patients requiring restoration of sinus rhythm
- Medications: Flecainide, propafenone, sotalol (if CAD present), amiodarone (if CHF present)
Anticoagulation
Indications assessed using CHA2DS2-VASc score
- DOAC (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban)
- Warfarin (INR 2-3)
Compare to risk of Bleeding with Anticoagulation using HASBLED
Surgical Intervention for Atrial Fibrillation
- Pulmonary vein isolation for severe cases
